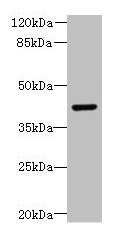
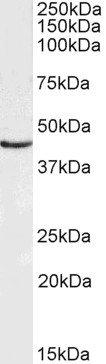
![WB analysis of human DCX recombinant protein using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. WB analysis of human DCX recombinant protein using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_WB_w_23061123_615.webp)
WB analysis of human DCX recombinant protein using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].
Doublecortin antibody [2G5]
GTX60612
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetDCX
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDoublecortin antibody [2G5]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1/500 - 1/2000. ICC/IF: 1/200 - 1/1000. IHC-P: 1/200 - 1/1000. FACS: 1/200 - 1/400. ELISA: 1/10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID2G5
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1641
- Target nameDCX
- Target descriptiondoublecortin
- Target synonymsDBCN, DC, LISX, SCLH, XLIS, neuronal migration protein doublecortin, doublecortex, doublin, lis-X, lissencephalin-X
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDO43602
- Protein NameNeuronal migration protein doublecortin
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the doublecortin family. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic protein and contains two doublecortin domains, which bind microtubules. In the developing cortex, cortical neurons must migrate over long distances to reach the site of their final differentiation. The encoded protein appears to direct neuronal migration by regulating the organization and stability of microtubules. In addition, the encoded protein interacts with LIS1, the regulatory gamma subunit of platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase, and this interaction is important to proper microtubule function in the developing cortex. Mutations in this gene cause abnormal migration of neurons during development and disrupt the layering of the cortex, leading to epilepsy, mental retardation, subcortical band heterotopia (double cortex syndrome) in females and lissencephaly (smooth brain syndrome) in males. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- András IE, Garcia-Contreras M, Yanick C, et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated amyloid transfer to neural progenitor cells: implications for RAGE and HIV infection. Mol Brain. 2020,13(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-0562-0Read this paper

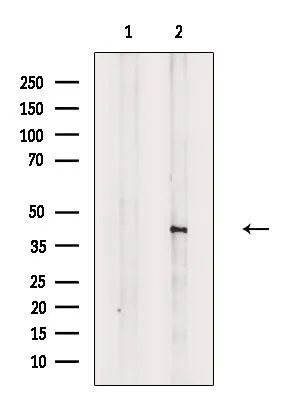
![WB analysis of Mouse heart lysate using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. WB analysis of Mouse heart lysate using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_WB_1_w_23061123_904.webp)
![FACS analysis of SK-N-SH cells using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. Green : Doublecortin Red : negative control FACS analysis of SK-N-SH cells using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. Green : Doublecortin Red : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_FACS_w_23061123_532.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of kidney cancer tissue using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. IHC-P analysis of kidney cancer tissue using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_IHC-P_1_w_23061123_339.webp)
![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_125.webp)
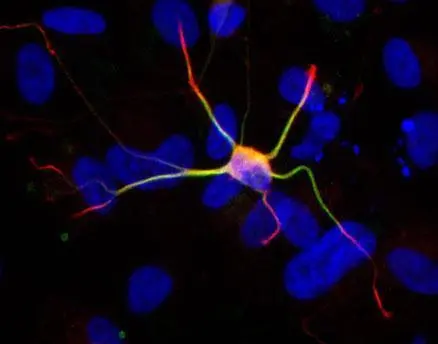
![ICC/IF analysis of HepG2 cells using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. Green : Doublecortin Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye ICC/IF analysis of HepG2 cells using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. Green : Doublecortin Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_ICCIF_w_23061123_594.webp)
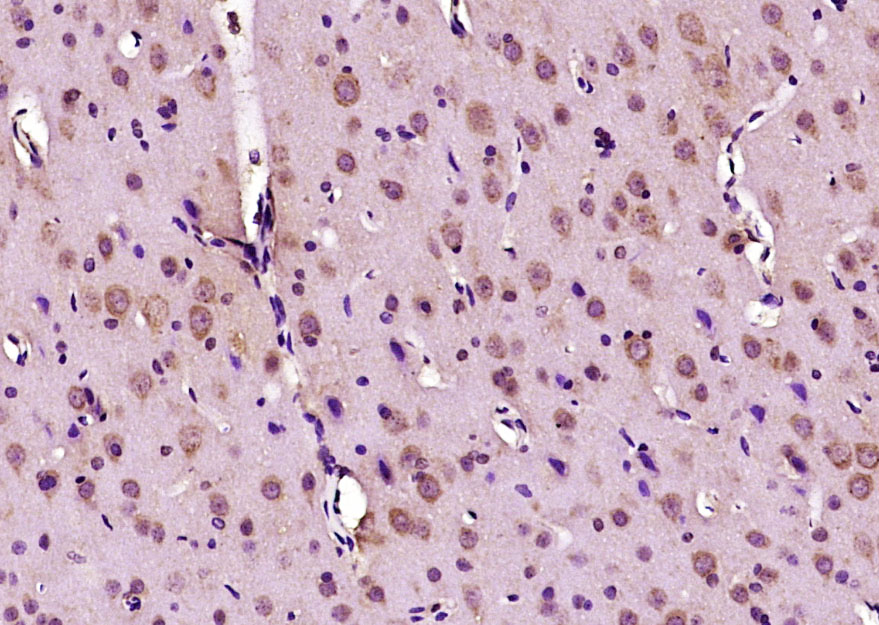
![IHC-P analysis of human brain tissue using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5]. IHC-P analysis of human brain tissue using GTX60612 Doublecortin antibody [2G5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60612/GTX60612_20170912_IHC-P_w_23061123_278.webp)