EGFR, Soluble (human) (rec.)
AG-40T-0041
Protein IDP00533
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameEGFR, Soluble (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID1956
- Target nameEGFR
- Target descriptionepidermal growth factor receptor
- Target synonymsERBB, ERBB1, ERRP, HER1, NISBD2, NNCIS, PIG61, mENA, epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR vIII, avian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-b) oncogene homolog, cell growth inhibiting protein 40, cell proliferation-inducing protein 61, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 1, proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1, receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1
- Protein IDP00533
- Protein NameEpidermal growth factor receptor
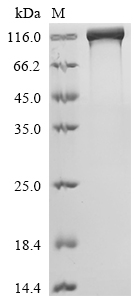
- Scientific DescriptionEGFR has been shown to bind a subset of the EGF family ligands, including EGF, amphiregulin, TGF-alpha, betacellulin, epiregulin, heparin-binding EGF and neuregulin-2 in the absence of a co-receptor. Ligand binding induces EGFR homodimerization as well as heterodimerization with ErbB2, resulting in kinase activation, tyrosine phosphorylation and cell signaling. EGFR signaling has been shown to regulate multiple biological functions including cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and apoptosis. In addition, EGFR signaling has also been shown to play a role in carcinogenesis. - Protein. Human EGFR (629aa) is fused at the C-terminus to a Strep-tag. Source: Sf9 cells. Lyophilized. Purity: >90% (SDS-PAGE). EGFR has been shown to bind a subset of the EGF family ligands, including EGF, amphiregulin, TGF-alpha, betacellulin, epiregulin, heparin-binding EGF and neuregulin-2 in the absence of a co-receptor. Ligand binding induces EGFR homodimerization as well as heterodimerization with ErbB2, resulting in kinase activation, tyrosine phosphorylation and cell signaling. EGFR signaling has been shown to regulate multiple biological functions including cell proliferation, differentiation, motility and apoptosis. In addition, EGFR signaling has also been shown to play a role in carcinogenesis.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman