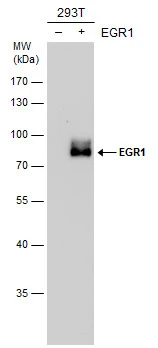
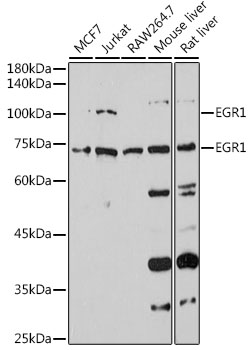
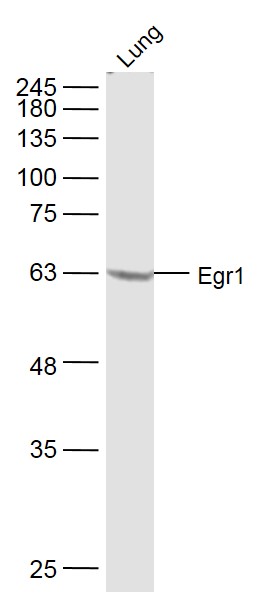
WB analysis of NIH-3T3 tissue lysate (35ug/lane) using GTX81956 EGR1 antibody, N-term.
EGR1 antibody, N-term
GTX81956
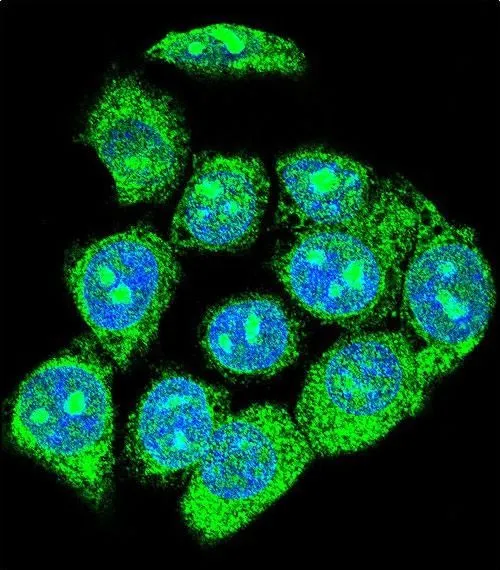
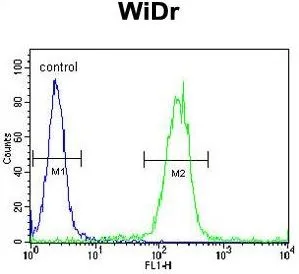
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetEGR1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameEGR1 antibody, N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. ICC/IF: 1:10-1:50. FCM: 1:10-1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1958
- Target nameEGR1
- Target descriptionearly growth response 1
- Target synonymsAT225, G0S30, KROX-24, NGFI-A, TIS8, ZIF-268, ZIF268, ZNF225, early growth response protein 1, EGR-1, nerve growth factor-induced protein A, transcription factor ETR103, transcription factor Zif268, zinc finger gene 225, zinc finger protein 225, zinc finger protein Krox-24
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP18146
- Protein NameEarly growth response protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the EGR family of C2H2-type zinc-finger proteins. It is a nuclear protein and functions as a transcriptional regulator. The products of target genes it activates are required for differentitation and mitogenesis. Studies suggest this is a cancer suppressor gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2014]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- REM sleep deprivation-induced circadian clock gene abnormalities participate in hippocampal-dependent memory impairment by enhancing inflammation in rats undergoing sevoflurane inhalation. Hou J et al., 2019 May 17, Behav Brain ResRead this paper

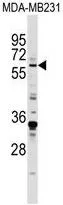


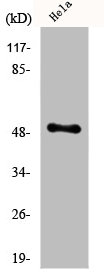

![WB analysis of EGR1(AA: 282-433)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 cell lysate using GTX83286 EGR1 antibody [8A6].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83286/GTX83286_20170912_WB_w_23061322_639.webp)