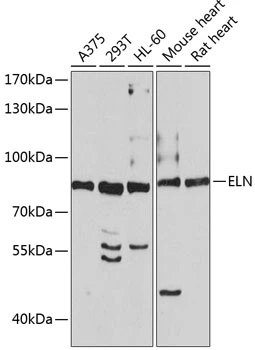
![IHC-P analysis of human small intestine tissue using GTX17734 Elastin antibody [ELN/1981]. IHC-P analysis of human small intestine tissue using GTX17734 Elastin antibody [ELN/1981].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX17734/GTX17734_20200115_IHC-P_1149_w_23060620_895.webp)
IHC-P analysis of human small intestine tissue using GTX17734 Elastin antibody [ELN/1981].
Elastin antibody [ELN/1981]
GTX17734
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetELN
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameElastin antibody [ELN/1981]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1-2microg/ml for 30 min at RT. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDELN/1981
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2006
- Target nameELN
- Target descriptionelastin
- Target synonymsADCL1, SVAS, WBS, WS, elastin, tropoelastin
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP15502
- Protein NameElastin
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein that is one of the two components of elastic fibers. Elastic fibers comprise part of the extracellular matrix and confer elasticity to organs and tissues including the heart, skin, lungs, ligaments, and blood vessels. The encoded protein is rich in hydrophobic amino acids such as glycine and proline, which form mobile hydrophobic regions bounded by crosslinks between lysine residues. Degradation products of the encoded protein, known as elastin-derived peptides or elastokines, bind the elastin receptor complex and other receptors and stimulate migration and proliferation of monocytes and skin fibroblasts. Elastokines can also contribute to cancer progression. Deletions and mutations in this gene are associated with supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS) and autosomal dominant cutis laxa. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161



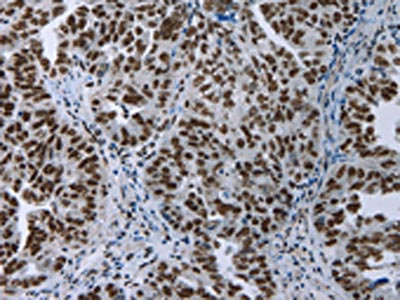

![IHC-P analysis of human small intestine tissue section using GTX02630 Elastin antibody [ELN/3131R].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX02630/GTX02630_20210319_IHC-P_w_23053122_932.webp)