ELISA Kit for Karyopherin Alpha 2 (KPNa2)
SEE748HU
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierCloud-Clone Corp.
- Product NameELISA Kit for Karyopherin Alpha 2 (KPNa2)
- Delivery Days Customer12
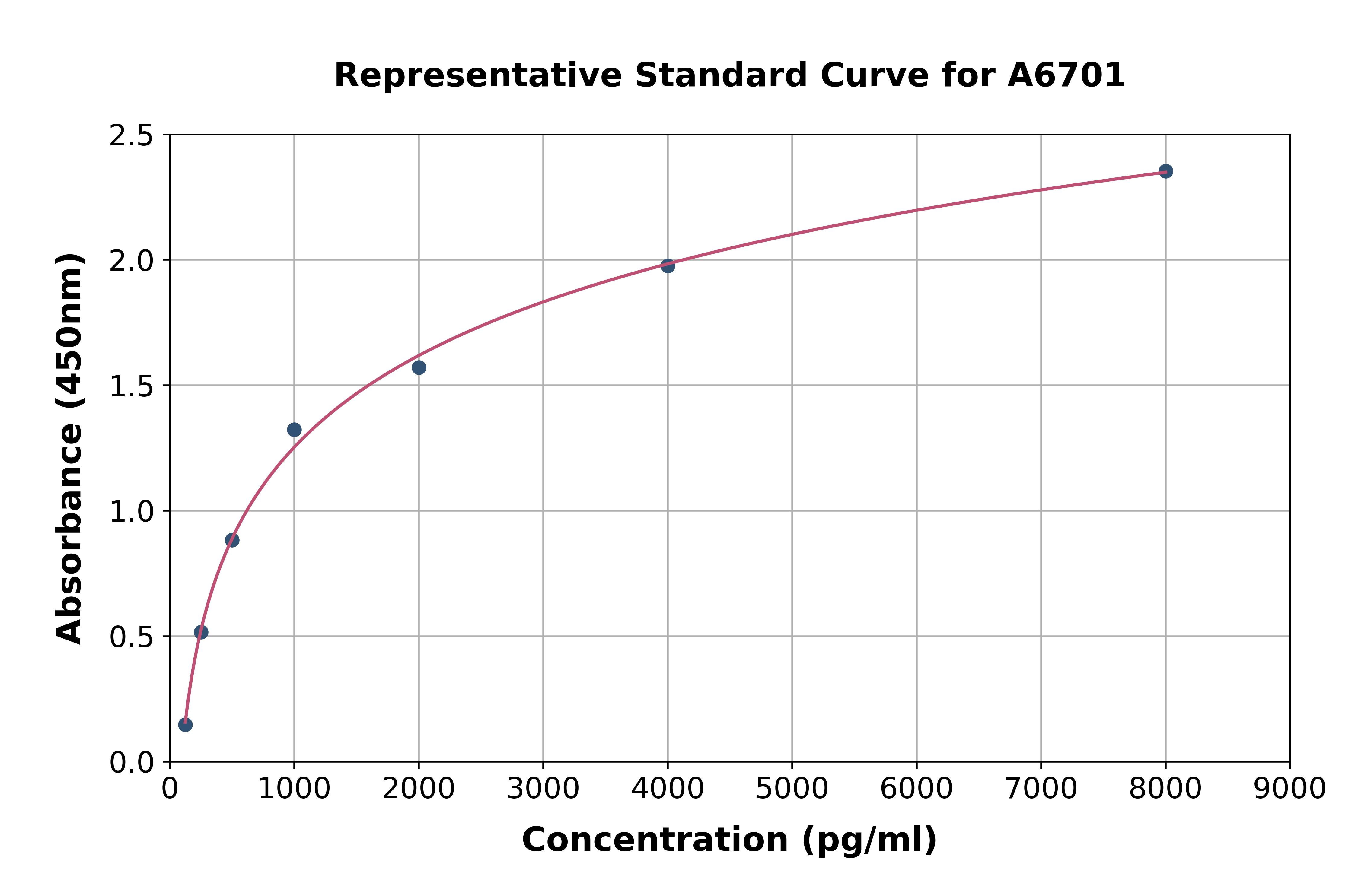
- ApplicationsELISA
- Assay Detection Range125-8,000pg/mL
- Assay PrecisionIntra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Karyopherin Alpha 2 (KPNa2) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle...
- Assay SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 55pg/mL
- Assay Test PrincipleThe test principle applied in this kit is Sandwich enzyme immunoassay. The microtiter plate provided in this kit has been pre-coated with an antibody specific to Karyopherin Alpha 2 (KPNa2). Standards or samples are then added to the appropriate...
- Assay Time3h
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Protein IDP52292
- Protein NameImportin subunit alpha-1
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman
References
- Nuclear transport proteins are secreted by cancer cells and identified as potential novel cancer biomarkers. van der Watt PJ et al., 2022 Jan 15, Int J CancerRead this paper
- Association of overexpressed karyopherin alpha 2 with poor survival and its contribution to interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression in oral cancer. Wang CI et al., 2018 Aug, Head NeckRead this paper
- KPNA2 is a potential diagnostic serum biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. Huang L et al., 2017 Jun, Tumour BiolRead this paper
- KPNA2 is a promising biomarker candidate for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and correlates with cell proliferation. Ma S et al., 2014 Oct, Oncol RepRead this paper