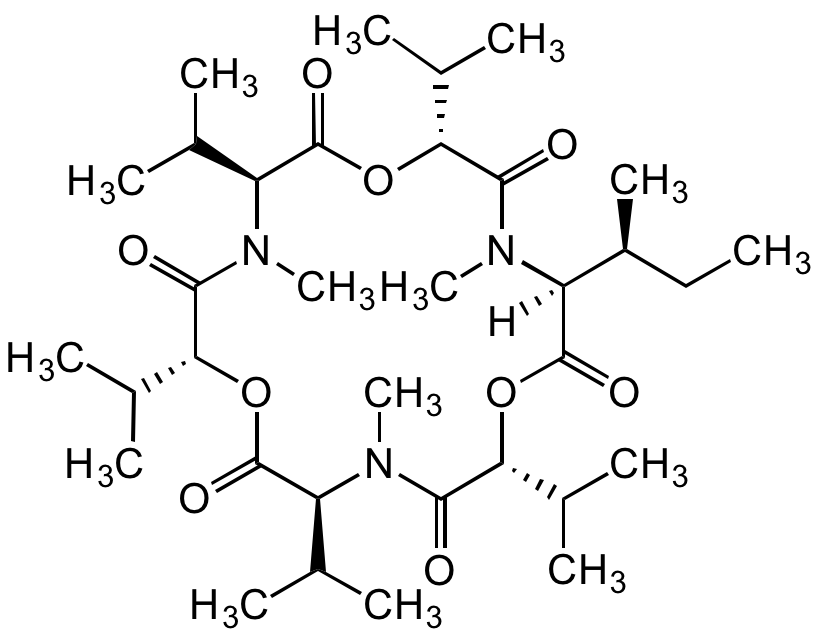
Chemical Structure
Enniatin B1 [19914-20-6] [19914-20-6]
AG-CN2-0480
CAS Number19914-20-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>96%
Molecular Weight653.9
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameEnniatin B1 [19914-20-6] [19914-20-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number19914-20-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>96%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC34H59N3O9
- Molecular Weight653.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 19914-20-6. Formula: C34H59N3O9. MW: 653.9. Isolated from fungus Fusarium sp. Cyclohexadepsipeptide mycotoxin. One of four major analogs in the enniatin complex. Commonly found food contaminant in cereals and their products. Ionophore antibiotic. Incorporation into the cell membrane forms dimeric structures that transport monovalent ions across the membrane (especially the mitochondrial membranes) affecting oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling. Anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis in several cancer cell lines, decreasing the activation of the cell proliferation kinase, ERK (p44/p42). Moderate inhibitor of ACAT (acylcoenzyme A:cholesterolacyl transferase). Inhibitor of the pleiotropic drug resistance protein 5 (Pdr5p) in yeast. Shown to have a variety of other biological activities such as antifungal, anthelmintic, insecticidal, immunomodulatory and phytotoxic activity. - Cyclohexadepsipeptide mycotoxin. One of four major analogs in the enniatin complex. Commonly found food contaminant in cereals and their products. Ionophore antibiotic. Incorporation into the cell membrane forms dimeric structures that transport monovalent ions across the membrane (especially the mitochondrial membranes) affecting oxidative phosphorylation uncoupling. Anticancer compound. Triggers apoptosis in several cancer cell lines, decreasing the activation of the cell proliferation kinase, ERK (p44/p42). Moderate inhibitor of ACAT (acylcoenzyme A:cholesterolacyl transferase). Inhibitor of the pleiotropic drug resistance protein 5 (Pdr5p) in yeast. Shown to have a variety of other biological activities such as antifungal, anthelmintic, insecticidal, immunomodulatory and phytotoxic activity.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1([C@@H](C)CC)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)N(C)C(=O)[C@H](OC1=O)C(C)C)C(C)C)C(C)C
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Enniatin B1 [19914-20-6] [19914-20-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/9C/CgoaEWayQWOEWqGPAAAAAK4yc9U480.png)