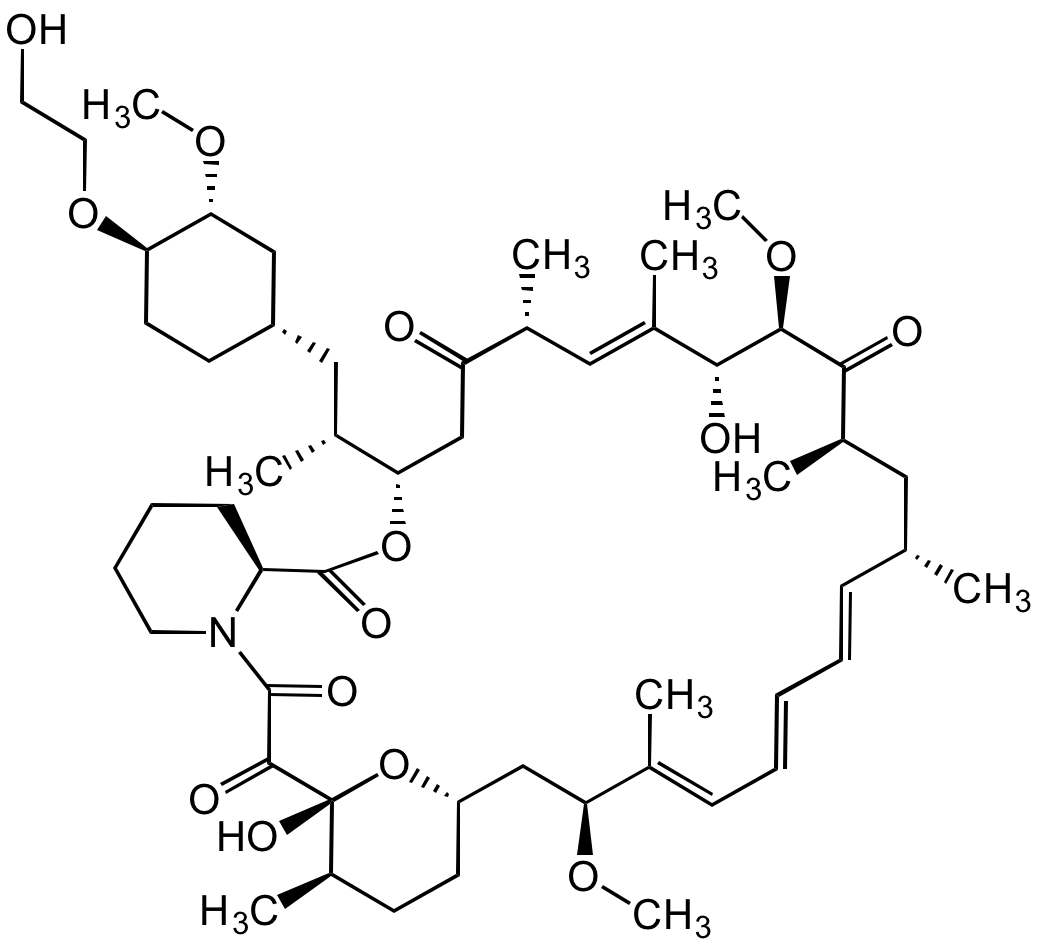
Chemical Structure
Everolimus [159351-69-6]
AG-CN2-0520
CAS Number159351-69-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight958.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameEverolimus [159351-69-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number159351-69-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationDanger
- Molecular FormulaC53H83NO14
- Molecular Weight958.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 159351-69-6. Formula: C53H83NO14. MW: 958.2. Isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Macrolide antibiotic, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Orally available Rapamycin derivative that shows improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Potent immunosuppressant. Binds with high affinity to the FK506 binding protein-12 (FKBP-12) to generate an immunosuppressive complex that inhibits the activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). More selective for the mTORC1 protein complex, with little impact on the mTORC2 complex, compared to Rapamycin. Since mTORC2 is believed to play an important role in glucose metabolism and the immune system, selective inhibition of mTORC1 achieves many of the benefits of rapamycin without the associated glucose intolerance and immunosuppression Anticancer agent. Inhibition of mTOR reduces the activity of effectors downstream, which leads to a blockage in the progression of cells from G1 into S phase, and subsequently inducing cell growth arrest, apoptosis and autophagy, resulting in reduction of cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose uptake. Inhibits tumor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Currently used as an immunosuppressant to prevent rejection of organ transplants and in the treatment of renal cell cancer and other tumours. - Macrolide antibiotic, inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Orally available rapamycin derivative that shows improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Potent immunosuppressant. Binds with high affinity to the FK506 binding protein-12 (FKBP12) to generate an immunosuppressive complex that inhibits the activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). More selective for the mTORC1 protein complex, with little impact on the mTORC2 complex, compared to rapamycin. Since mTORC2 is believed to play an important role in glucose metabolism and the immune system, selective inhibition of mTORC1 achieves many of the benefits of rapamycin without the associated glucose intolerance and immunosuppression Anticancer agent. Inhibition of mTOR reduces the activity of effectors downstream, which leads to a blockage in the progression of cells from G1 into S phase, and subsequently inducing cell growth arrest, apoptosis and autophagy, resulting in reduction of cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose uptake. Inhibits tumor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Used as an immunosuppressant to prevent rejection of organ transplants and in the treatment of renal cell cancer and other tumors.
- SMILESOCCO[C@@H]1CC[C@@H](C[C@H]([C@@H]2CC([C@@H](/C=C([C@H]([C@H](C([C@@H](C[C@@H](/C=C/C=C/C=C([C@H](C[C@@H]3CC[C@H]([C@@](O3)(C(C(N4CCCC[C@H]4C(O2)=O)=O)=O)O)C)OC)\C)C)C)=O)OC)O)\C)C)=O)C)C[C@H]1OC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

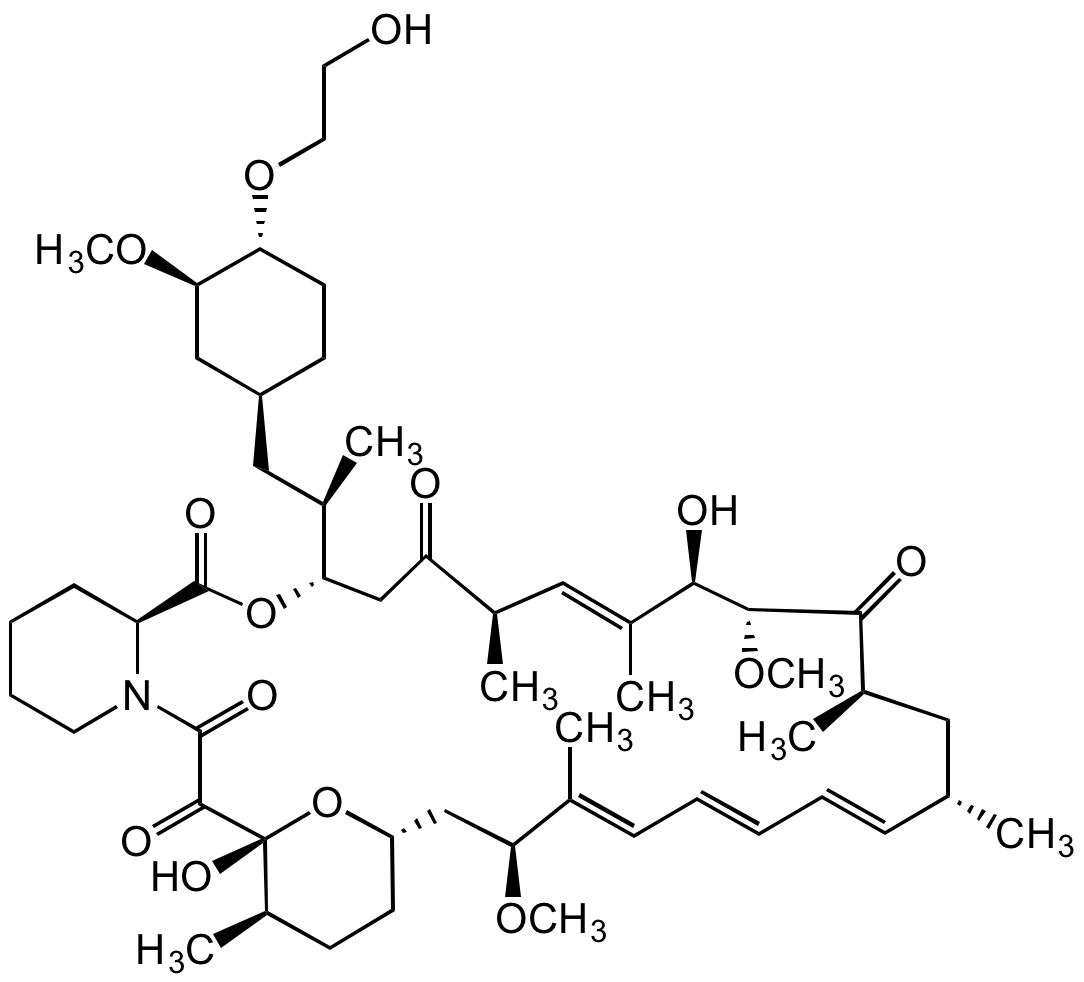

![Everolimus [159351-69-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/37/33/CgoaEGaySW6EfO-MAAAAAO061BM886.png)