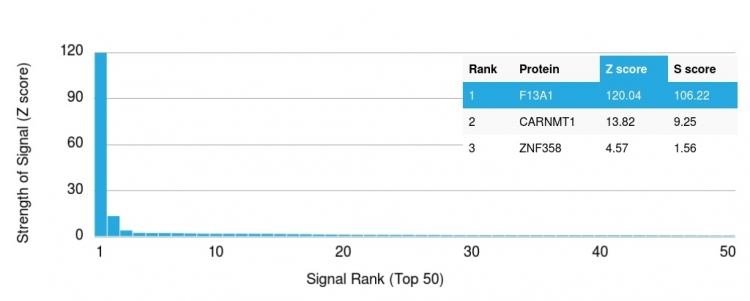
![WB analysis of recombinant Factor XIIIa protein and HeLa cell lysates using GTX34714 Factor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1448]. WB analysis of recombinant Factor XIIIa protein and HeLa cell lysates using GTX34714 Factor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1448].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34714/GTX34714_20200115_WB_1864_w_23060801_420.webp)
WB analysis of recombinant Factor XIIIa protein and HeLa cell lysates using GTX34714 Factor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1448].
Factor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1448]
GTX34714
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetF13A1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameFactor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1448]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-2microg/ml. ICC/IF: 1-2microg/ml. IHC-P: 1-2microg/ml for 30 min at RT. FACS: 1-2microg/106 cells. ELISA: 2-4microg/ml (for coating). *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDF13A1/1448
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2162
- Target nameF13A1
- Target descriptioncoagulation factor XIII A chain
- Target synonymsF13A, coagulation factor XIII A chain, FSF, A subunit, TGase, bA525O21.1 (coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide), coagulation factor XIII, A polypeptide, coagulation factor XIII, A1 polypeptide, coagulation factor XIIIa, factor XIIIa, fibrin stabilizing factor, A subunit, fibrinoligase, protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase A chain, transglutaminase A chain, transglutaminase. plasma
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP00488
- Protein NameCoagulation factor XIII A chain
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the coagulation factor XIII A subunit. Coagulation factor XIII is the last zymogen to become activated in the blood coagulation cascade. Plasma factor XIII is a heterotetramer composed of 2 A subunits and 2 B subunits. The A subunits have catalytic function, and the B subunits do not have enzymatic activity and may serve as plasma carrier molecules. Platelet factor XIII is comprised only of 2 A subunits, which are identical to those of plasma origin. Upon cleavage of the activation peptide by thrombin and in the presence of calcium ion, the plasma factor XIII dissociates its B subunits and yields the same active enzyme, factor XIIIa, as platelet factor XIII. This enzyme acts as a transglutaminase to catalyze the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine crosslinking between fibrin molecules, thus stabilizing the fibrin clot. It also crosslinks alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor, or fibronectin, to the alpha chains of fibrin. Factor XIII deficiency is classified into two categories: type I deficiency, characterized by the lack of both the A and B subunits; and type II deficiency, characterized by the lack of the A subunit alone. These defects can result in a lifelong bleeding tendency, defective wound healing, and habitual abortion. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203


![IHC-P analysis of human lymph node tissue using GTX04452 Factor XIIIa antibody [MSVA-813R] HistoMAX?. Strong factor XIII immunostaining of sinus histiocytes in a lymph node.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04452/GTX04452_20230728_IHC-P_53_23072722_488.webp)

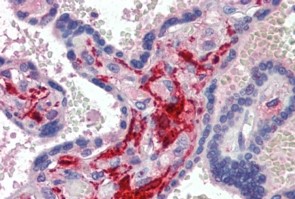

![IHC-P analysis of human histiocytoma tissue using GTX34716 Factor XIIIa antibody [F13A1/1683].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34716/GTX34716_20200115_IHC-P_622_w_23060801_286.webp)