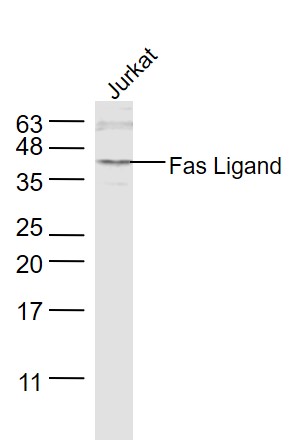
Fas Ligand antibody [NOK-1]
GTX01476
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetFASLG
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameFas Ligand antibody [NOK-1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier Note*Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDNOK-1
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID356
- Target nameFASLG
- Target descriptionFas ligand
- Target synonymsALPS1B, APT1LG1, APTL, CD178, CD95-L, CD95L, FASL, TNFSF6, TNLG1A, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6, CD95 ligand, Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6), apoptosis (APO-1) antigen ligand 1, apoptosis antigen ligand, fas antigen ligand, mutant tumor necrosis factor family member 6, tumor necrosis factor ligand 1A
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP48023
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily. The primary function of the encoded transmembrane protein is the induction of apoptosis triggered by binding to FAS. The FAS/FASLG signaling pathway is essential for immune system regulation, including activation-induced cell death (AICD) of T cells and cytotoxic T lymphocyte induced cell death. It has also been implicated in the progression of several cancers. Defects in this gene may be related to some cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161





![FACS analysis of human CD178 (Fas ligand) transfected cells using GTX01476-02 Fas Ligand antibody [NOK-1] (Biotin). Solid lone : primary antibody Dashed line : isotype control antibody amount : 0.25 μg (5 μl)](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX01476-02/GTX01476-02_20200428_FACS63_w_23053121_534.webp)
![FACS analysis of human CD178 (Fas ligand) transfected cells using GTX01476-07 Fas Ligand antibody [NOK-1] (APC). Solid lone : primary antibody Dashed line : isotype control antibody amount : 0.25 μg (5 μl)](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX01476-07/GTX01476-07_20200428_FACS37_w_23053121_512.webp)
![FACS analysis of human CD178 (Fas ligand) transfected cells using GTX01476-08 Fas Ligand antibody [NOK-1] (PE). Solid lone : primary antibody Dashed line : isotype control antibody amount : 0.5 μg (5 μl)](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX01476-08/GTX01476-08_20200428_FACS132_w_23053121_383.webp)