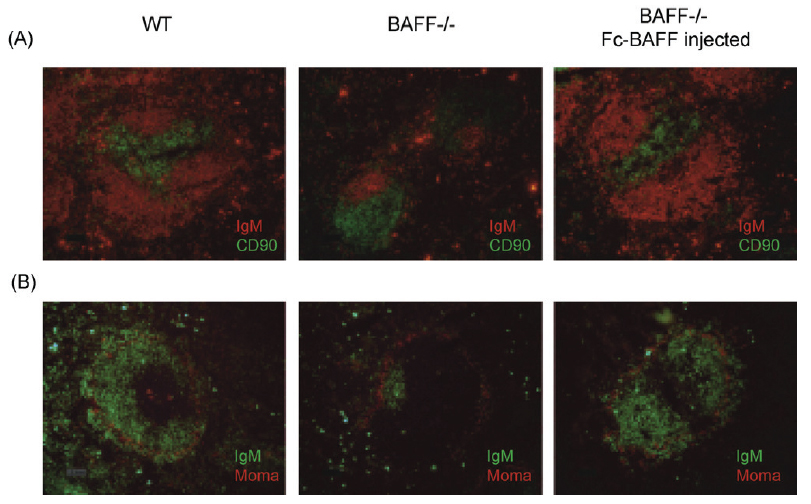
Restoration of the splenic T and B cell architecture in Fc-BAFF injected BAFFdeficient mice. BAFF deficient mice were injected at day 0 with 100mg BAFF (human):Fc (human) (AG-40B-0120) intravenously and at day 14 with 50mg BAFF (human):Fc (human) intraper
Fc (human):BAFF (human) (rec.)
AG-40B-0120
Protein IDQ9Y275
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameFc (human):BAFF (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID10673
- Target nameTNFSF13B
- Target descriptionTNF superfamily member 13b
- Target synonymsBAFF, BLYS, CD257, DTL, TALL-1, TALL1, THANK, TNFSF20, TNLG7A, ZTNF4, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B, ApoL related ligand TALL-1, B-cell-activating factor, B-lymphocyte stimulator, Delta4 BAFF, TNF and ApoL-related leukocyte expressed ligand 1, TNF homolog that activates apoptosis, delta BAFF, dendritic cell-derived TNF-like molecule, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b, tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 20, tumor necrosis factor ligand 7A, tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 13b, tumor necrosis factor-like protein ZTNF4
- Protein IDQ9Y275
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 13B
- Scientific DescriptionBAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells. T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells and also non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF. BAFF binds three distinct receptors (BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA) expressed predominantly on B cells, although activated T cells also express BAFF-R. BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival, and together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Deregulated expression of BAFF leads to autoimmune disorders in mice. In humans, elevated levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases such as Sjoegren syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). BAFF has also increased levels in some lymphoid cancers. - Protein. The receptor-binding domain of human BAFF (aa 136-285) is fused at the N-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1. Source: CHO cells. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). BAFF is mainly produced by innate immune cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells. T cells, activated B cells, some malignant B cells and also non-lymphoid cells like astrocytes, synoviocytes and epithelial cells can also produce BAFF. BAFF binds three distinct receptors (BAFF-R, TACI and BCMA) expressed predominantly on B cells, although activated T cells also express BAFF-R. BAFF is a master regulator of peripheral B cell survival, and together with IL-6, promotes Ig class-switching and plasma cell differentiation. Besides its major role in B cell biology, BAFF co-stimulates activated T cells. Deregulated expression of BAFF leads to autoimmune disorders in mice. In humans, elevated levels of soluble BAFF have been detected in the serum of patients with various autoimmune diseases such as Sjoegren syndrome, Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). BAFF has also increased levels in some lymphoid cancers.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman