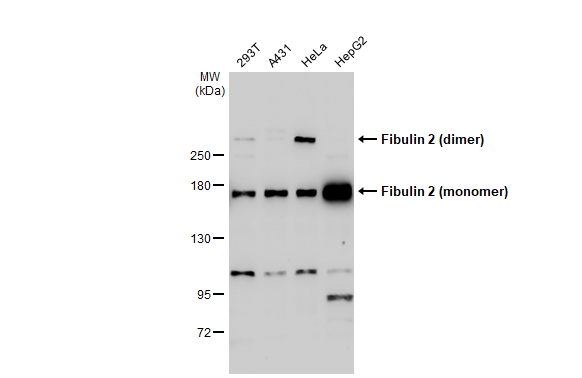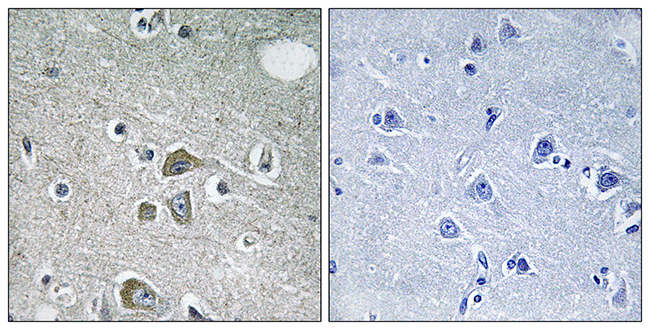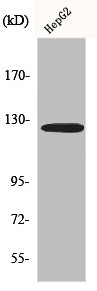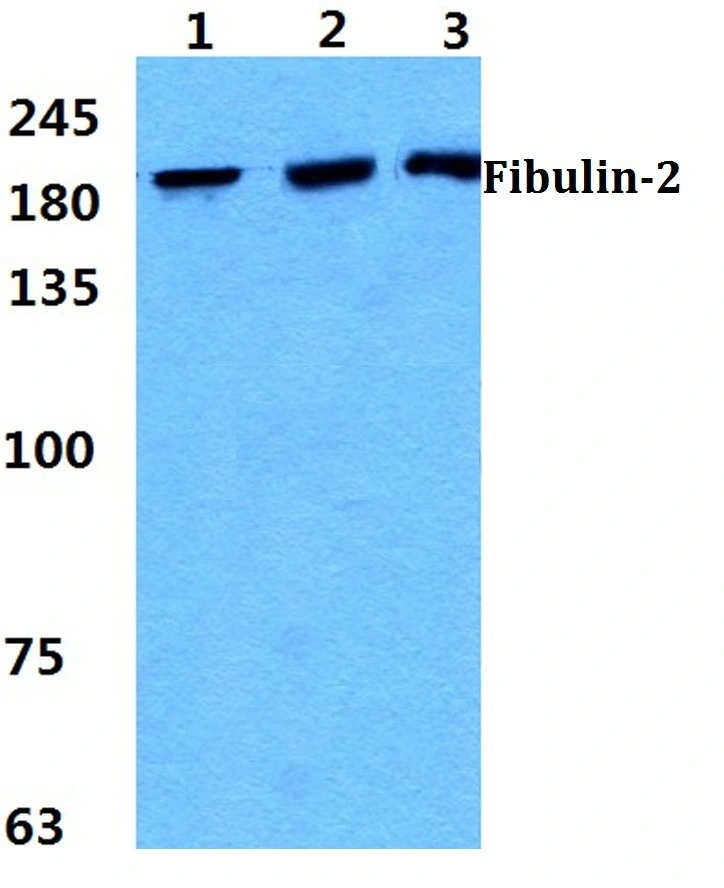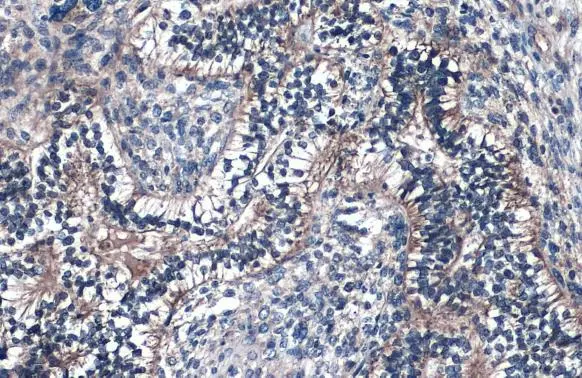
Fibulin 2 antibody detects Fibulin 2 protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human endometrial carcinoma. Fibulin 2 stained by Fibulin 2 antibody (GTX105108) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Fibulin 2 antibody
GTX105108
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
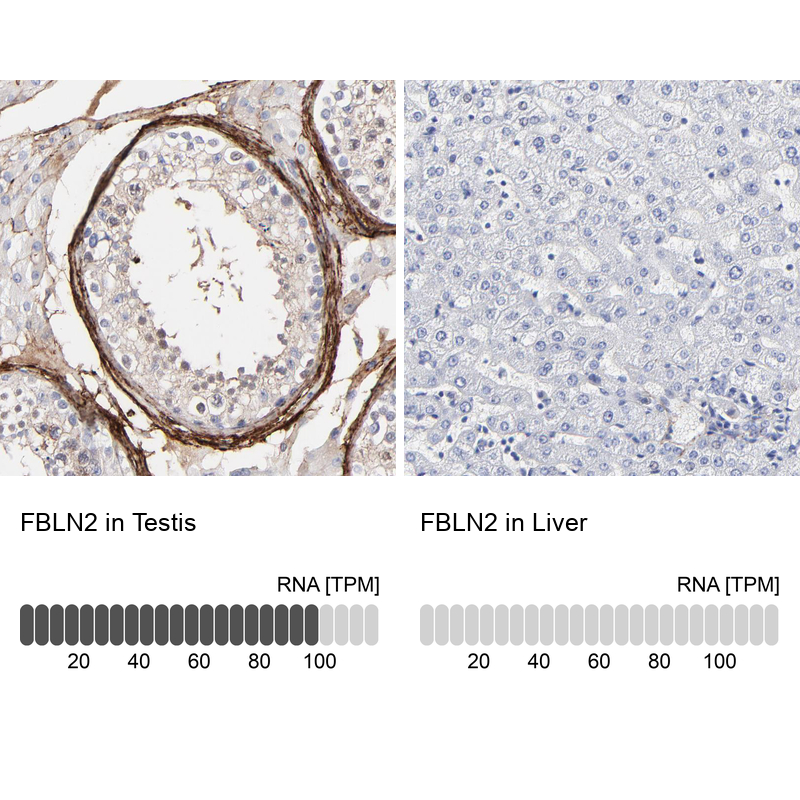
TargetFBLN2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameFibulin 2 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.19 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2199
- Target nameFBLN2
- Target descriptionfibulin 2
- Target synonymsfibulin-2, FIBL-2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP98095
- Protein NameFibulin-2
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes an extracellular matrix protein, which belongs to the fibulin family. This protein binds various extracellular ligands and calcium. It may play a role during organ development, in particular, during the differentiation of heart, skeletal and neuronal structures. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161