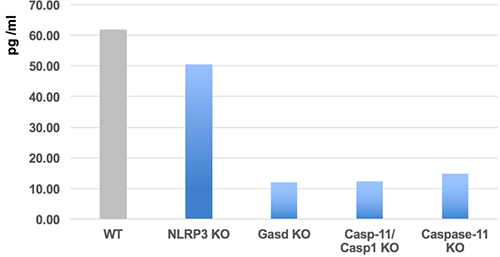
Specificity
Gasdermin D (mouse) ELISA Kit
AG-45B-0011
ReactivityMouse
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGasdermin D (mouse) ELISA Kit
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsELISA
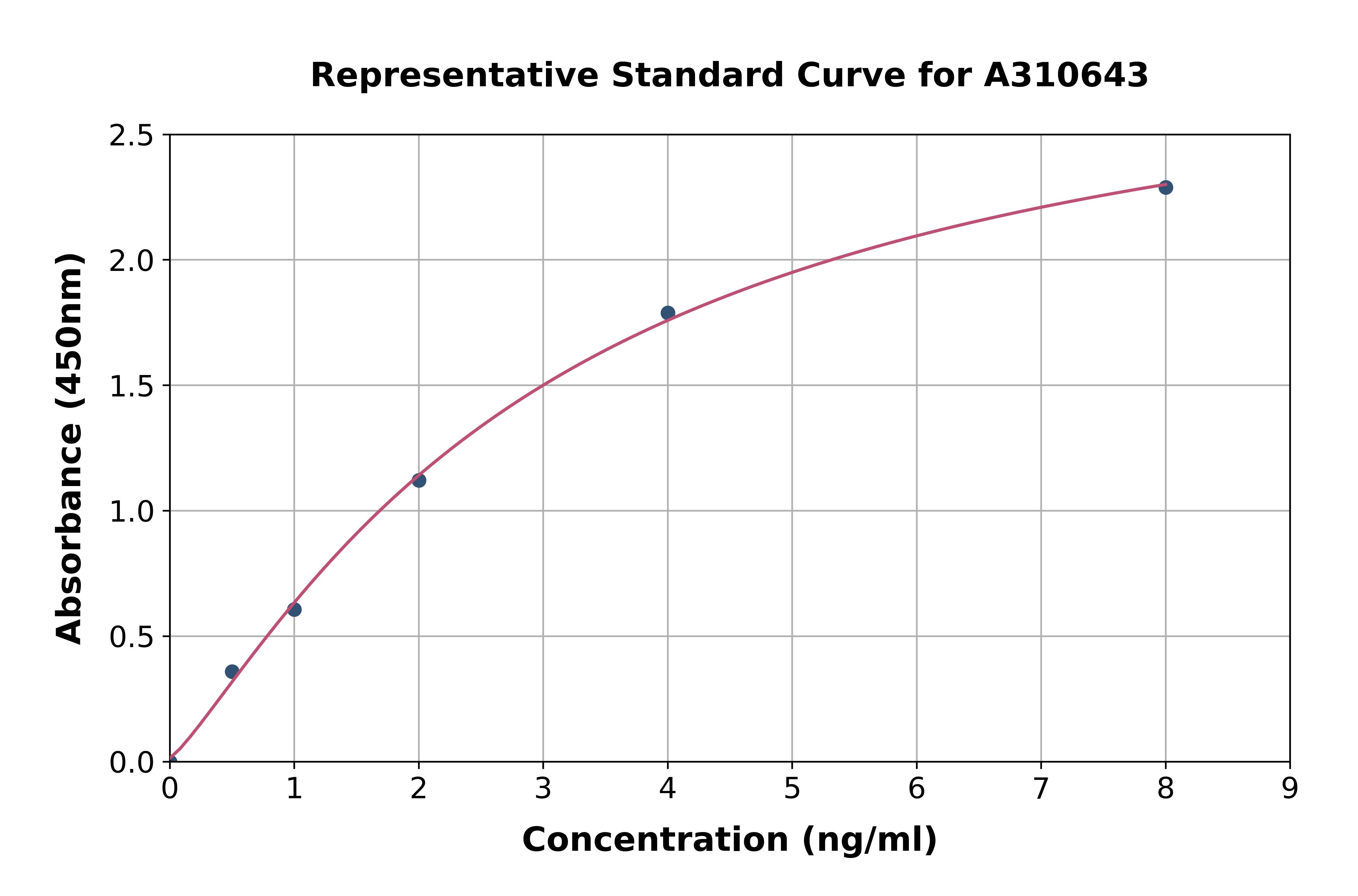
- Assay Detection Range15.6 to 1000pg/ml
- Assay Sensitivity14pg/ml
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Protein IDQ9D8T2
- Protein NameGasdermin-D
- Scientific DescriptionELISA assay. Detects full-length and cleaved mouse Gasdermin D (C-terminus) in cell culture supernatants and cell extracts. Does not cross-react with human gasdermin D. Colorimetric sandwich assay. Sample Type: Cell Culture Supernatant, Cell Lysate. Range: 15.6 to 1000pg/ml. Sensitivity: 14pg/ml. Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that comprise a sensor (e.g. NLRP3), an adaptor (ASC/Pycard) and the procaspase-1. An inflammasome assembles in response to a diverse range of pathogen-associated or danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs). The inflammasome platform leads to activation of caspase-1, which further induces maturation of interleukin-1beta and -18 (IL-1beta and IL-18) through proteolytic cleavage of pro-IL-1beta and pro-IL-18. Activated caspase-1, and also the recently characterized caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome pathway, also cleave the intracellular gasdermin D, which leads to a particular form of inflammatory cell death called pyroptosis. The gasdermin family members contain N-terminal domains that are capable of forming membrane pores to induce cytolysis, whereas the C-terminal domains of gasdermins function as inhibitors of such cytolysis through intramolecular domain association. Caspase-1 or -11 cleavage of gasdermin D is required for regulation of pyroptosis: upon protease cleavage of the gasdermin N- and C-domain linker, the disruption of the intramolecular domain interaction in the presence of lipids releases the N-domain to assemble oligomeric membrane pores that trigger cell death. Gasdermin D seems to be a key effector in the LPS-induced lethal sepsis. - Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that comprise a sensor (e.g. NLRP3), an adaptor (ASC/Pycard) and the procaspase-1. An inflammasome assembles in response to a diverse range of pathogen-associated or danger-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs). The inflammasome platform leads to activation of caspase-1, which further induces maturation of interleukin-1beta and -18 (IL-1beta and IL-18) through proteolytic cleavage of pro-IL-1beta and pro-IL-18. Activated caspase-1, and also the recently characterized caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome pathway, also cleave the intracellular gasdermin D, which leads to a particular form of inflammatory cell death called pyroptosis. The gasdermin family members contain N-terminal domains that are capable of forming membrane pores to induce cytolysis, whereas the C-terminal domains of gasdermins function as inhibitors of such cytolysis through intramolecular domain association. Caspase-1 or -11 cleavage of gasdermin D is required for regulation of pyroptosis: upon protease cleavage of the gasdermin N- and C-domain linker, the disruption of the intramolecular domain interaction in the presence of lipids releases the N-domain to assemble oligomeric membrane pores that trigger cell death. Gasdermin D seems to be a key effector in the LPS-induced lethal sepsis.
- ReactivityMouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesMouse