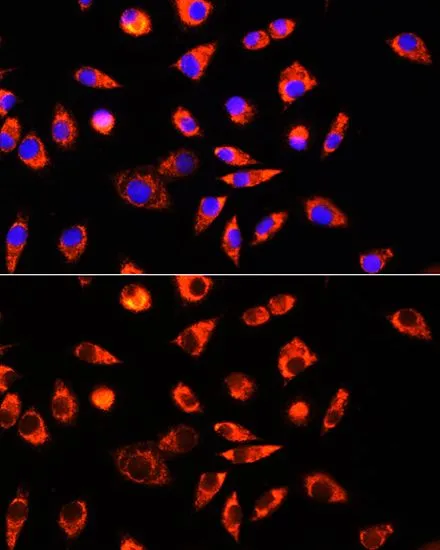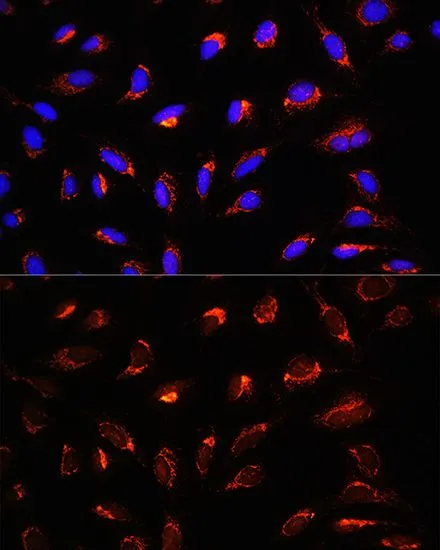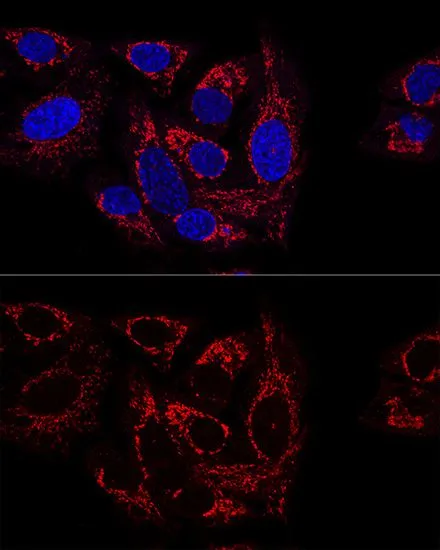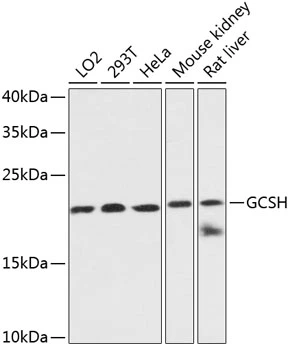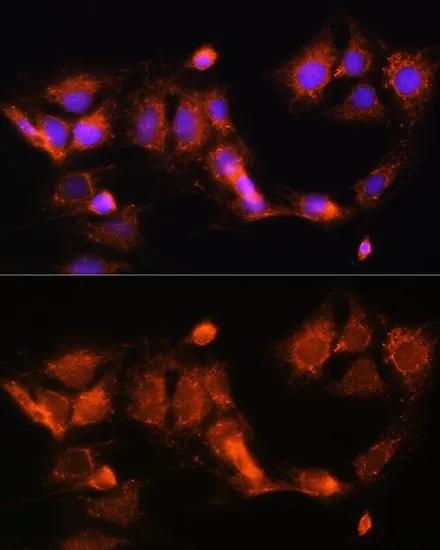
ICC/IF analysis of C6 cells using GTX66196 GCSH antibody. Blue : DAPI Dilution : 1:100
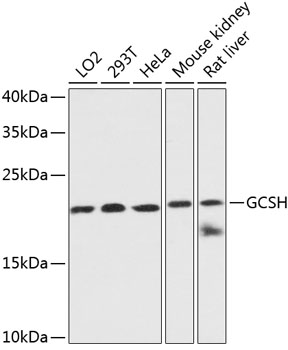
GCSH antibody
GTX66196
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetGCSH
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGCSH antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2653
- Target nameGCSH
- Target descriptionglycine cleavage system protein H
- Target synonymsGCE, MMDS7, NKH, glycine cleavage system H protein, mitochondrial, glycine cleavage system protein H (aminomethyl carrier), lipoic acid-containing protein, mitochondrial glycine cleavage system H-protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP23434
- Protein NameGlycine cleavage system H protein, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionDegradation of glycine is brought about by the glycine cleavage system, which is composed of four mitochondrial protein components: P protein (a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent glycine decarboxylase), H protein (a lipoic acid-containing protein), T protein (a tetrahydrofolate-requiring enzyme), and L protein (a lipoamide dehydrogenase). The protein encoded by this gene is the H protein, which transfers the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein to the T protein. Defects in this gene are a cause of nonketotic hyperglycinemia (NKH). Two transcript variants, one protein-coding and the other probably not protein-coding,have been found for this gene. Also, several transcribed and non-transcribed pseudogenes of this gene exist throughout the genome.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161