GITRL, Soluble (human) (rec.)
CHI-AG-40A-0019
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierChimerigen Laboratories
- Product NameGITRL, Soluble (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
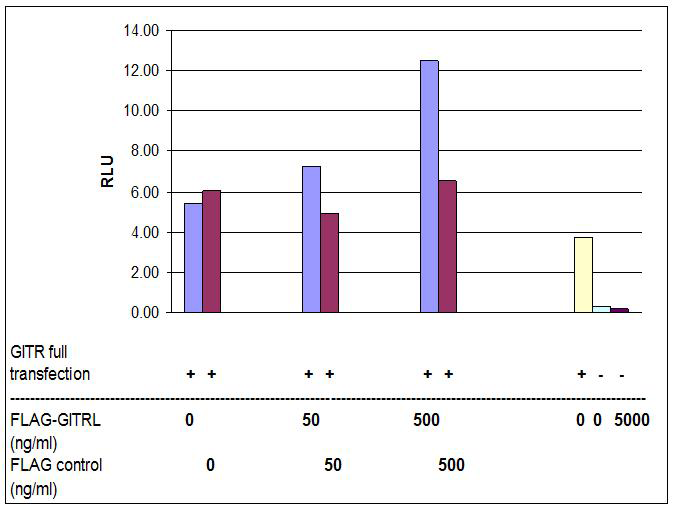
- Scientific DescriptionGITRL (Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor ligand) is expressed on dendritic cells (DC), monocytes, macrophages, B cells, activated T cells, endothelial cells, osteoclasts and various healthy non-lymphoid tissues (e.g. testis). GITRL is constitutively expressed and released as soluble form by solid tumors and various hematopoietic malignancies. GITRL causes differentiation of osteoclasts, activation of macrophages, but also alteration of carcinoma and leukemia cells and influences apoptosis. Binding to GITR is important in regulating T cell proliferation and TCR-mediated apoptosis. GITRL is implicated in development of autoimmune diseases and in the immune response against infectious pathogens and tumors. - Protein. The extracellular domain of human GITRL (aa 74-199) is fused at the N-terminus to a FLAG®-tag. Source: HEK 293 cells. Endotoxin content: 90% (SDS-PAGE). GITRL (Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor ligand) is expressed on dendritic cells (DC), monocytes, macrophages, B cells, activated T cells, endothelial cells, osteoclasts and various healthy non-lymphoid tissues (e.g. testis). GITRL is constitutively expressed and released as soluble form by solid tumors and various hematopoietic malignancies. GITRL causes differentiation of osteoclasts, activation of macrophages, but also alteration of carcinoma and leukemia cells and influences apoptosis. Binding to GITR is important in regulating T cell proliferation and TCR-mediated apoptosis. GITRL is implicated in development of autoimmune diseases and in the immune response against infectious pathogens and tumors.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman