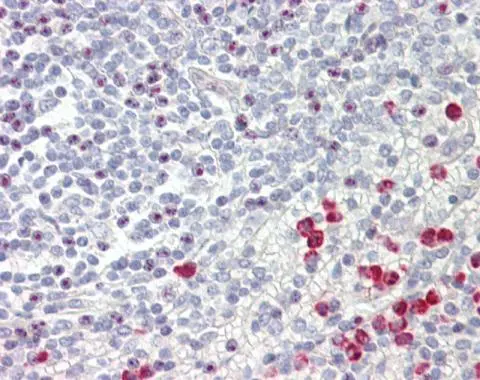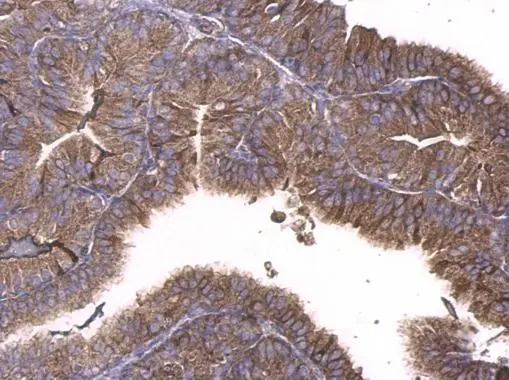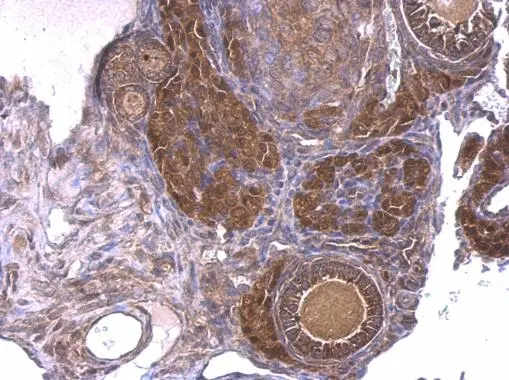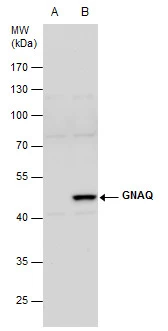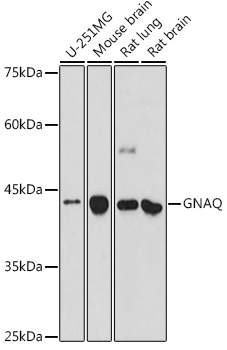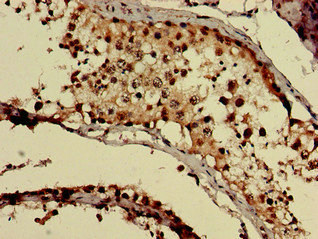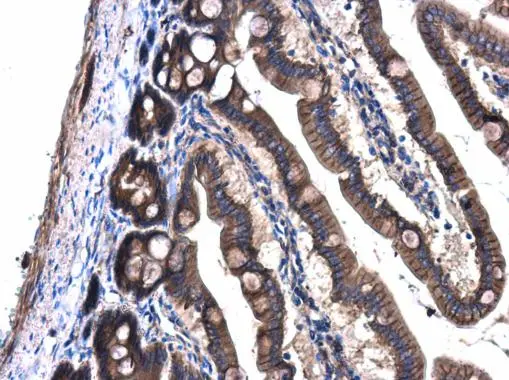
GNAQ antibody detects GNAQ protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm in rat intestine by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat intestine. GNAQ antibody (GTX104544) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
GNAQ antibody
GTX104544
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetGNAQ
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGNAQ antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2776
- Target nameGNAQ
- Target descriptionG protein subunit alpha q
- Target synonymsCMAL, CMC1, G-ALPHA-q, GAQ, SWS, guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), q polypeptide, guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP50148
- Protein NameGuanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha
- Scientific DescriptionGuanine nucleotide-binding proteins are a family of heterotrimeric proteins that couple cell surface, 7-transmembrane domain receptors to intracellular signaling pathways. Receptor activation catalyzes the exchange of GTP for GDP bound to the inactive G protein alpha subunit resulting in a conformational change and dissociation of the complex. The G protein alpha and beta-gamma subunits are capable of regulating various cellular effectors. Activation is terminated by a GTPase intrinsic to the G-alpha subunit. G-alpha-q is the alpha subunit of one of the heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins that mediates stimulation of phospholipase C-beta (MIM 600230).[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161