![GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] detects GNAT1 protein expression by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen sectioned adult mouse retina. Green: GNAT1 protein stained by GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX105960) diluted at 1:250. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] detects GNAT1 protein expression by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen sectioned adult mouse retina. Green: GNAT1 protein stained by GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX105960) diluted at 1:250. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX105960/GTX105960_40562_20170214_IHC-Fr_w_23060120_747.webp)
GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] detects GNAT1 protein expression by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen sectioned adult mouse retina. Green: GNAT1 protein stained by GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX105960) diluted at 1:250. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ TUJ1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
GNAT1 antibody [N1C3]
GTX105960
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetGNAT1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGNAT1 antibody [N1C3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-Fr: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.34 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2779
- Target nameGNAT1
- Target descriptionG protein subunit alpha transducin 1
- Target synonymsCSNB1G, CSNBAD3, GBT1, GNATR, HG1F, guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-1, guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein), alpha transducing activity polypeptide 1, guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(T), alpha-1 subunit, heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide-binding protein 1F, rod-type transducin alpha subunit, transducin alpha-1 chain, transducin, rod-specific
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP11488
- Protein NameGuanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-1
- Scientific DescriptionTransducin is a 3-subunit guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) which stimulates the coupling of rhodopsin and cGMP-phoshodiesterase during visual impulses. The transducin alpha subunits in rods and cones are encoded by separate genes. This gene encodes the alpha subunit in rods. This gene is also expressed in other cells, and has been implicated in bitter taste transduction in rat taste cells. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal dominant congenital stationary night blindness. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Various tissue extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX105960) diluted at 1:3000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various tissue extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with GNAT1 antibody [N1C3] (GTX105960) diluted at 1:3000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX105960/GTX105960_44482_20211105_WB_M_tissue_w_23060120_441.webp)
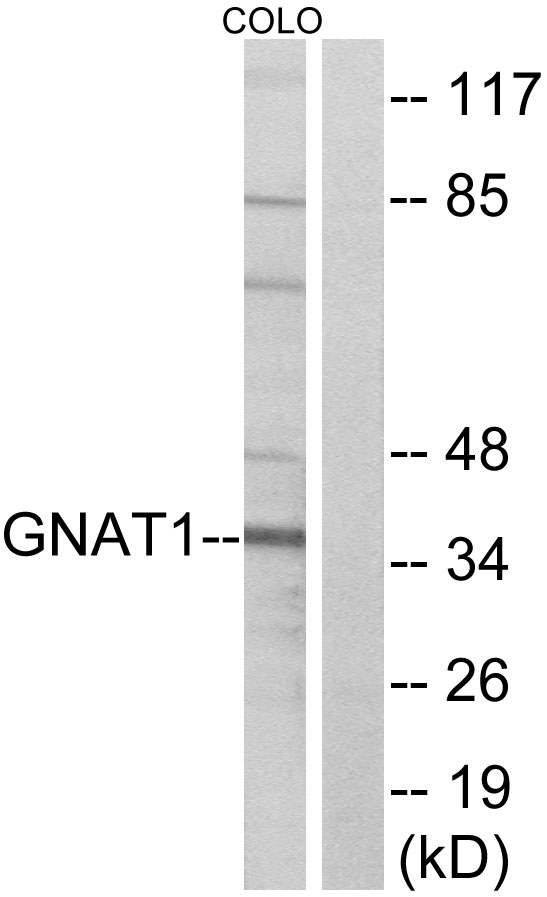



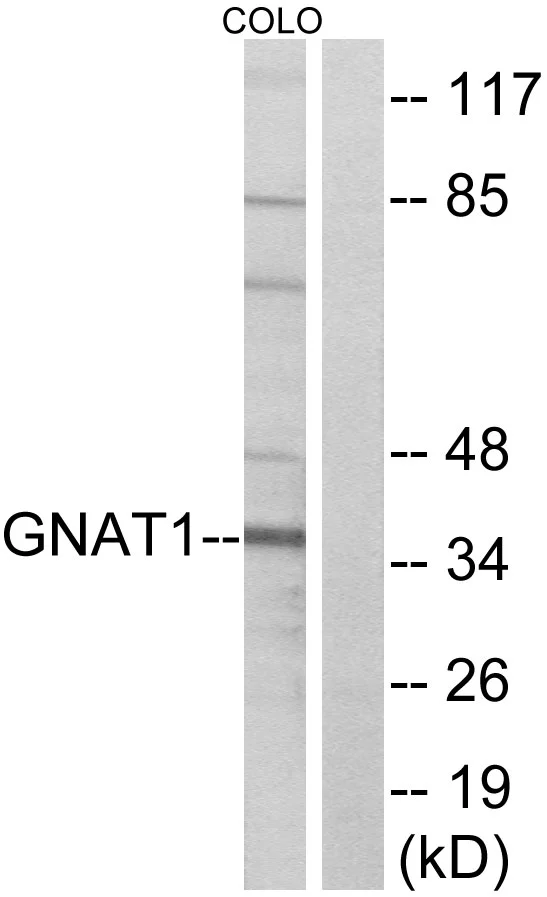

![Non-transfected and transfected 293T whole cell extracts were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with GNAT1 antibody [HL2126] (GTX638098) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638098/GTX638098_T-44914_20231103_WB_multiple_B_23110819_721.webp)