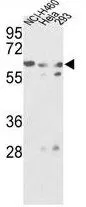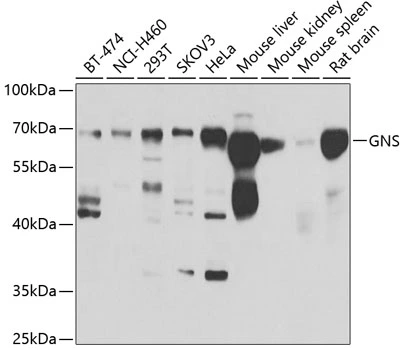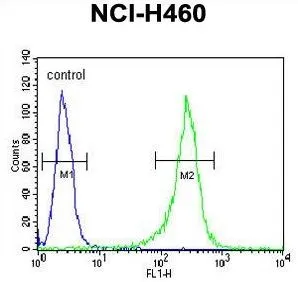
FACS analysis of NCI-H460 cells using GTX81833 GNS antibody, Internal. Green : primary antibody Blue : negative control
GNS antibody, Internal
GTX81833
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetGNS
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGNS antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. IHC-P: 1:50-1:100. FCM: 1:10-1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2799
- Target nameGNS
- Target descriptionglucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase
- Target synonymsG6S, N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase, glucosamine -6-sulfatase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP15586
- Protein NameN-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase
- Scientific DescriptionThe product of this gene is a lysosomal enzyme found in all cells. It is involved in the catabolism of heparin, heparan sulphate, and keratan sulphate. Deficiency of this enzyme results in the accumulation of undegraded substrate and the lysosomal storage disorder mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID (Sanfilippo D syndrome). Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIID is the least common of the four subtypes of Sanfilippo syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Hypoxia Induces Autophagy through Translational Up-Regulation of Lysosomal Proteins in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Lai MC et al., 2016, PLoS OneRead this paper