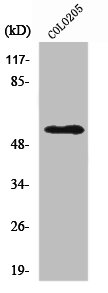
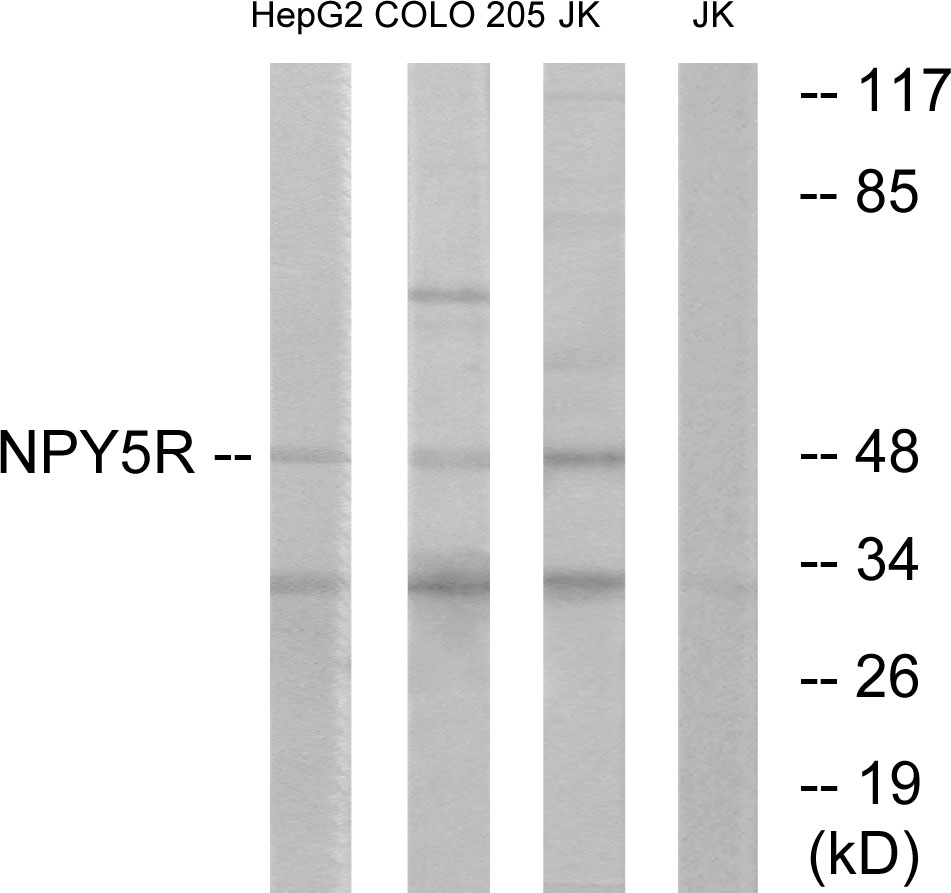
Goat anti-Neuropeptide Y receptor Y5
EB06769
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Hamster, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetNPY5R
Overview
- SupplierEverest Biotech
- Product NameGoat anti-Neuropeptide Y receptor Y5
- Delivery Days Customer5
- Application Supplier NoteImmunoprecipitation: Customer feedback showed specific results when this product was used in IP. This antibody has been successfully used in IP: PMID: 30503694.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- Applications SupplierPep-ELISA, WB, IP, IHC
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- Gene ID4889
- Target nameNPY5R
- Target descriptionneuropeptide Y receptor Y5
- Target synonymsNPY5-R, NPYR5, NPYY5-R, neuropeptide Y receptor type 5, NPY-Y5 receptor, Y5 receptor
- HostGoat
- Scientific DescriptionRefSeq number(s): NP_006165.1. GeneIDs all Nonhuman: 18168 (mouse); 25340 (rat);. Purification: Antigen affinity purified. Names and symbols: neuropeptide Y receptor Y5 ; HGNC:7958; NPY5R; NPYR5
- ReactivityCanine, Hamster, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Reactivity SupplierHuman, Mouse, Rat, Dog
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Czarnecka M, Lu C, Pons J, et al. Neuropeptide Y receptor interactions regulate its mitogenic activity. Neuropeptides. 2019,73:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2018.11.008Read this paper
- Czarnecka M, Kitlinska J. Cell Surface Protein Detection to Assess Receptor Internalization. Bio Protoc. 2016,6(20):pii: e1968. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1968.Read this paper
- Sheriff S, Ali M, Yahya A, et al. Neuropeptide Y Y5 receptor promotes cell growth through extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling and cyclic AMP inhibition in a human breast cancer cell line. Mol Cancer Res. 2010,8(4):604-14. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0301Read this paper