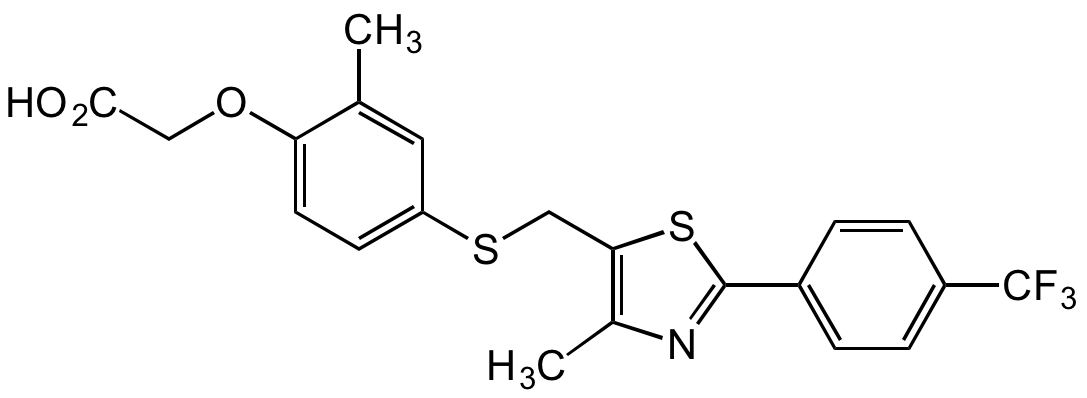
Chemical Structure
GW501516 [317318-70-0] [317318-70-0]
AG-CR1-3641
CAS Number317318-70-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight453.5
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGW501516 [317318-70-0] [317318-70-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number317318-70-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC21H18F3NO3S2
- Molecular Weight453.5
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 317318-70-0. Formula: C21H18F3NO3S2. MW: 453.5. Potent and selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) delta agonist/activator with high affinity (Ki=1nM) and potency (EC50=1nM) for PPARdelta and >1000 fold selectivity over PPARalpha and PPARgamma. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR delta) has emerged as an important regulator of lipid homeostasis and inflammatory signaling. Recent in vitro, in vivo and human clinical studies have highlighted a role for PPARdelta activation in the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Antidiabetic compound. Shown to activate pathways initiated through exercise and was investigated as a potential treatment for obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease. Off-target high doses lead to tumor progression in rodents. Increases ABC A1 transporter expression and induces apolipoprotein A1-mediated cholesterol efflux in vitro. Increase serum HDL cholesterol and lowers small-dense LDL levels in obesity in vivo models. Reduces plasma triglyceride concentration. Increases expression of genes involved in lipid utilization, beta-oxidation, cholesterol efflux and energy uncoupling, as well as apolipoprotein-A1 specific efflux of intracellular cholesterol, indicating the muscle tissue is an important target. Model compound for a new type of obesity therapeutic, as well as a selective pharmacological tool for understanding lipid metabolism. - Potent and selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) delta agonist/activator with high affinity (Ki=1nM) and potency (EC50=1nM) for PPARdelta and >1000 fold selectivity over PPARalpha and PPARgamma. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPAR delta) has emerged as an important regulator of lipid homeostasis and inflammatory signaling. Recent in vitro, in vivo and human clinical studies have highlighted a role for PPARdelta activation in the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Antidiabetic compound. Shown to activate pathways initiated through exercise and was investigated as a potential treatment for obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease. Off-target high doses lead to tumor progression in rodents. Increases ABC A1 transporter expression and induces apolipoprotein A1-mediated cholesterol efflux in vitro. Increase serum HDL cholesterol and lowers small-dense LDL levels in obesity in vivo models. Reduces plasma triglyceride concentration. Increases expression of genes involved in lipid utilization, beta-oxidation, cholesterol efflux and energy uncoupling, as well as apolipoprotein-A1 specific efflux of intracellular cholesterol, indicating the muscle tissue is an important target. Model compound for a new type of obesity therapeutic, as well as a selective pharmacological tool for understanding lipid metabolism.
- SMILESCC1=CC(SCC2=C(C)N=C(C3=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C3)S2)=CC=C1OCC(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![GW 501516 [317318-70-0] [317318-70-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/C6/CgoaEWY7N-aEb0M7AAAAAKfIlsk141.png)