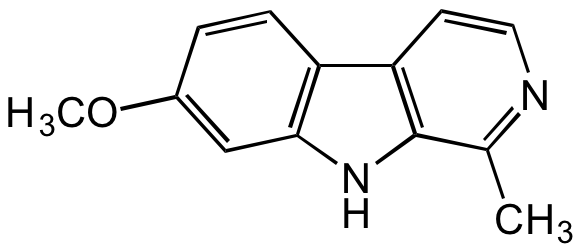
Chemical Structure
Harmine [442-51-3]
AG-CN2-0510
CAS Number442-51-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight212.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameHarmine [442-51-3]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number442-51-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC13H12N2O
- Molecular Weight212.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 442-51-3. Formula: C13H12N2O. MW: 212.3. Synthetic. Originally isolated from the seeds of Peganum harmala (Syrian rue). Fluorescent beta-carboline alkaloid. Potent ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of DYRK1A, DYRK2 and DYRK3 with IC50 values of 0.08, 0.9 and 0.8microM. Shown to inhibit CLK2, PIM3 (at 4.3microM) and CK1 at 1.5microM as well. Inhibits DYRK1A-mediated tau phosphorylation. Competitive and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that reversibly inhibits MAO-A (monoamine oxidase A) but has no effect on MAO-B. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI). Could potentially ameliorate impaired memory. Useful fluorescent pH indicator. Shows a color change from pH 7.2 (blue fluorescence) to pH 8.9 (yellow fluorescence). With the radioisotope carbon-11, used in positron emission tomography neuroimaging to examine its binding to MAO-A. Antiviral and antileishmanial compound. Antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Inhibits cellular proliferation, migration, invasion and induced apoptosis in vitro, as well as inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Antidiabetic. Unique regulator of PPARgamma expression that acts by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway in a cell-specific manner. Induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Reduced blood glucose, free fatty acids and triglyceride levels, delayed hyperglycemia and improved insulin sensitivity. Shown to induce adipocyte thermogenesis through the RAC1-MEK-ERK-CHD4 axis. CHD4 directly binds the proximal promoter region of UCP1, serving as a negative modulator of UCP1 and inducing browing in brown (BAT) and white adipose tissue (WAT). Inhibits DNA topoisomerases and interferes with DNA synthesis. Interacts with DNA via both groove binding and intercalative modes and cause major DNA structural changes. Shown to promote differentiation of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and chondrocytes (cells in the cartilage) and to inhibit osteoclastogenesis (the formation of bone resorbing cells). Antimalarial by inhibiting the Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 90 (PfHSP90) ATP-binding domain. - Fluorescent beta-carboline alkaloid. Potent ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of DYRK1A, DYRK2 and DYRK3 with IC50 values of 0.08, 0.9 and 0.8microM. Shown to inhibit CLK2, PIM3 (at 4.3microM) and CK1 at 1.5microM as well. Inhibits DYRK1A-mediated tau phosphorylation. Competitive and reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) that reversibly inhibits MAO-A (monoamine oxidase A) but has no effect on MAO-B. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (AChEI). Could potentially ameliorate impaired memory. Useful fluorescent pH indicator. Shows a color change from pH 7.2 (blue fluorescence) to pH 8.9 (yellow fluorescence). With the radioisotope carbon-11, used in positron emission tomography neuroimaging to examine its binding to MAO-A. Antiviral and antileishmanial compound. Antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Inhibits cellular proliferation, migration, invasion and induced apoptosis in vitro, as well as inhibited tumor growth in vivo. Antidiabetic. Unique regulator of PPARgamma expression that acts by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway in a cell-specific manner. Induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Reduced blood glucose, free fatty acids and triglyceride levels, delayed hyperglycemia and improved insulin sensitivity. Shown to induce adipocyte thermogenesis through the RAC1-MEK-ERK-CHD4 axis. CHD4 directly binds the proximal promoter region of UCP1, serving as a negative modulator of UCP1 and inducing browning in brown (BAT) and white adipose tissue (WAT). Inhibits DNA topoisomerases and interferes with DNA synthesis. Interacts with DNA via both groove binding and intercalative modes and cause major DNA structural changes. Shown to promote differentiation of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) and chondrocytes (cells in the cartilage) and to inhibit osteoclastogenesis (the formation of bone resorbing cells). Antimalarial by inhibiting the Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 90 (PfHSP90) ATP-binding domain.
- SMILESCC1=NC=CC2=C1NC3=C2C=CC(OC)=C3
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Harmine [442-51-3]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/37/E1/CgoaEWayU0OEann8AAAAAC5XH7M096.png)