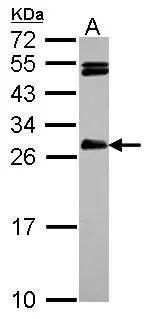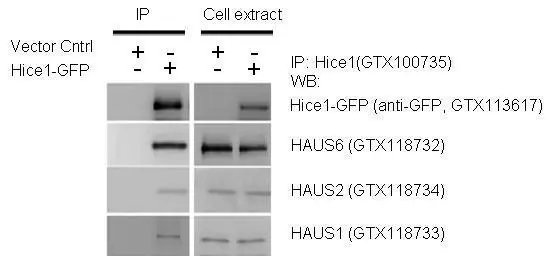
IP-WB assay to show that Hice1 (GTX113617) co-immunoprecipitated with other Augmin components HAUS6 (GTX118732), HAUS2 (GTX118734) and HAUS1 (GTX118733) in U2OS cells.
HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2]
GTX118734
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHAUS2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID55142
- Target nameHAUS2
- Target descriptionHAUS augmin like complex subunit 2
- Target synonymsC15orf25, CEP27, HsT17025, HAUS augmin-like complex subunit 2, centrosomal protein 27kDa, centrosomal protein of 27 kDa
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9NVX0
- Protein NameHAUS augmin-like complex subunit 2
- Scientific DescriptionHAUS2 is 1 of 8 subunits of the 390-kD human augmin complex, or HAUS complex. The augmin complex was first identified in Drosophila, and its name comes from the Latin verb augmentare, meaning to increase. The augmin complex is a microtubule-binding complex involved in microtubule generation within the mitotic spindle and is vital to mitotic spindle assembly (Goshima et al., 2008 [PubMed 18443220]; Uehara et al., 2009 [PubMed 19369198]).[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Ustinova K, Ruhnow F, Gili M, et al. Microtubule binding of the human augmin complex is directly controlled by importins and Ran-GTP. J Cell Sci. 2023,136(12). doi: 10.1242/jcs.261096Read this paper
- Tsai CY, Ngo B, Tapadia A, et al. Aurora-A phosphorylates Augmin complex component Hice1 protein at an N-terminal serine/threonine cluster to modulate its microtubule binding activity during spindle assembly. J Biol Chem. 2011,286(34):30097-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.266767Read this paper

![HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] detects HAUS2 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: HAUS2 protein stained by HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] (GTX118734) diluted at 1:1000. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] detects HAUS2 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: HAUS2 protein stained by HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] (GTX118734) diluted at 1:1000. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX118734/GTX118734_40198_20150410_IFA_w_23060519_884.webp)
![HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] detects HAUS2 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: A431 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: HAUS2 protein stained by HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] (GTX118734) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33343 staining. HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] detects HAUS2 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: A431 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: HAUS2 protein stained by HAUS2 antibody [N1C3-2] (GTX118734) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33343 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX118734/GTX118734_40198_IFA_w_23060519_219.webp)