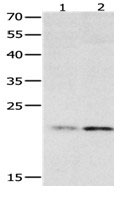
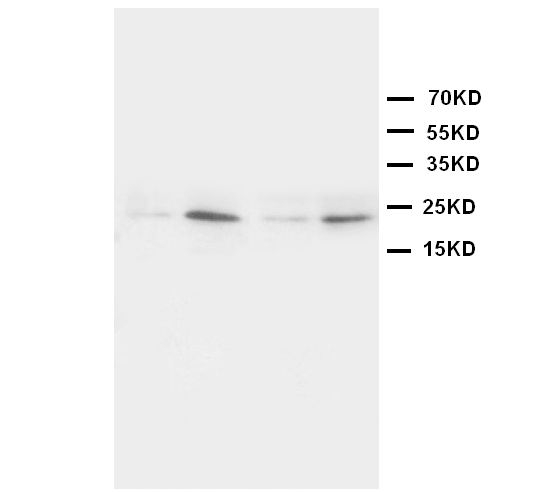
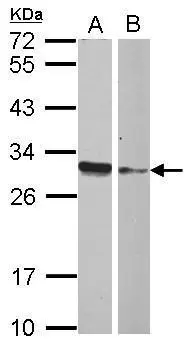
Gel: 12%SDS-PAGE, Lysate: 40 ug, Lane 1-2: 231 cells, human fetal liver tissue, Primary antibody: CSB-PA049190(HMGB4 Antibody) at dilution 1/500, Secondary antibody: Goat anti rabbit IgG at 1/8000 dilution, Exposure time: 2 minutes
HMGB4 Antibody
CSB-PA049190
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHMGB4
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameHMGB4 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID127540
- Target nameHMGB4
- Target descriptionhigh mobility group box 4
- Target synonymsdJ1007G16.5, high mobility group protein B4, HMG2 like
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8WW32
- Protein NameHigh mobility group protein B4
- Scientific DescriptionHigh mobility group protein B4 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the HMGB4 gene.HMGB4 is strongly and preferentially expressed in the adult mouse testis and weakly in the brain, but not in many other tissues. HMGB4 associates with chromatin, and in transfection assays, in contrast to HMGB1, it acts as a potent transcriptional repressor. During spermatogenesis, HMGB4 is present in the euchromatin of late pachytene spermatocytes and haploid round spermatids, whereas stronger expression is observed during the elongation phase, where it localizes to the basal pole of the nucleus in a manner mutually exclusive with H1FNT (H1T2) localized at the apical pole. HMGB4 basal localization is lost in H1FNT-mutant spermatids, showing that H1FNT provides a positional cue for organizing chromatin domains within the nucleus. These results show that HMGB4 and H1FNT specify distinct chromatin domains at the apical and basal poles of the elongating spermatid nucleus.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161