Human BD-4 / beta Defensin-4 ELISA kit
ARG80902
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierArigo Biolaboratories
- Product NameHuman BD-4 / beta Defensin-4 ELISA kit
- Delivery Days Customer23
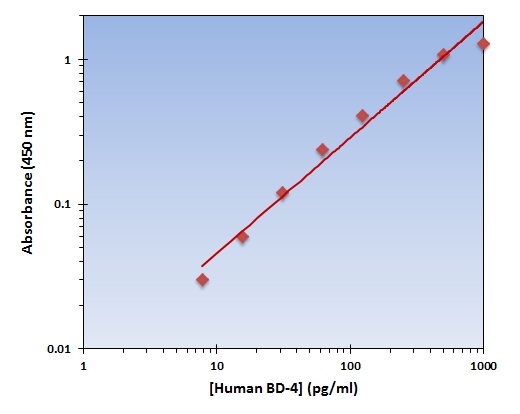
- ApplicationsELISA
- Assay PrecisionCV: less than10%
- Assay Sensitivity0.8 pg/ml
- Assay Time4 hours
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateHRP
- Protein IDQ8WTQ1
- Protein NameBeta-defensin 104
- Scientific DescriptionDefensins are 2-6 kDa, cationic, microbicidal peptides active against many Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, fungi, and enveloped viruses [PMID: 8528769], containing three pairs of intramolecular disulphide bonds. On the basis of their size and pattern of disulphide bonding, mammalian defensins are classified into alpha, beta and theta categories. Every mammalian species explored thus far has beta-defensins. In cows, as many as 13 beta-defensins exist in neutrophils. However, in other species, beta-defensins are more often produced by epithelial cells lining various organs (e.g. the epidermis, bronchial tree and genitourinary tract). Defensins are produced constitutively and/or in response to microbial products or proinflammatory cytokines. Some defensins are also called corticostatins (CS) because they inhibit corticotropin-stimulated corticosteroid production. The mechanism(s) by which microorganisms are killed and/or inactivated by defensins is not understood completely. However, it is generally believed that killing is a consequence of disruption of the microbial membrane. The polar topology of defensins, with spatially separated charged and hydrophobic regions, allows them to insert themselves into the phospholipid membranes so that their hydrophobic regions are buried within the lipid membrane interior and their charged (mostly cationic) regions interact with anionic phospholipid head groups and water. Subsequently, some defensins can aggregate to form channel-like pores; others might bind to and cover the microbial membrane in a carpet-like manner. The net outcome is the disruption of membrane integrity and function, which ultimately leads to the lysis of microorganisms. Some defensins are synthesised as propeptides which may be relevant to this process. [provide by Interpro: IPR006080]
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman