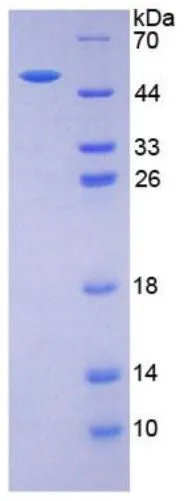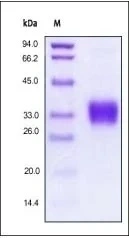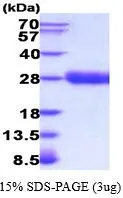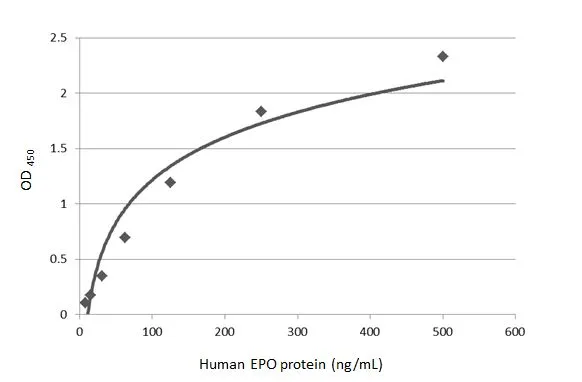
Indirect ELISA analysis was performed by coating the plate with recombinant E.coli expressed, full-length human EPO protein, His and GST tag (active) (GTX00422-pro) (500-7.81 ng/mL). Coated protein was probed with EPO antibody (GTX100813) (1 μg/mL). Goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) (1:10000) was used to detect the bound primary antibody.
Human EPO protein, His and GST tag (active)
GTX00422-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay, ELISA
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP01588
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman EPO protein, His and GST tag (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
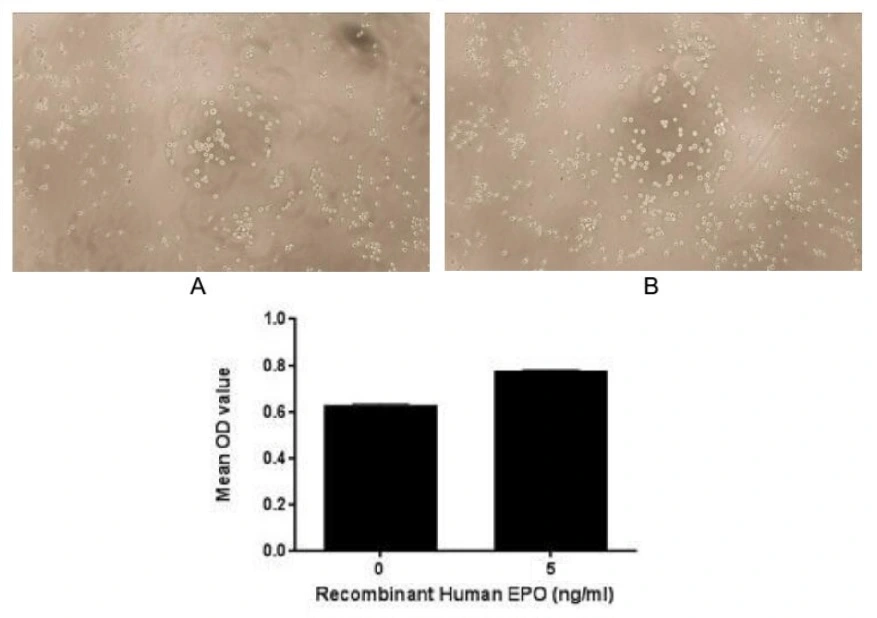
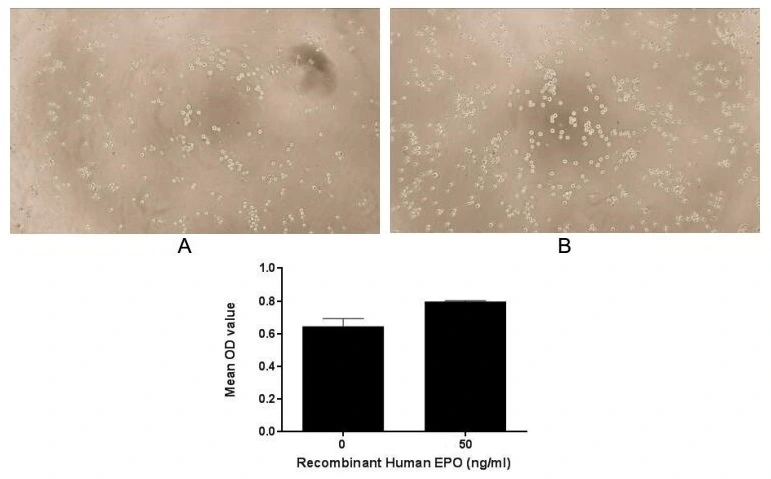
- Application Supplier NoteErythropoietin (EPO), also known as hematopoietin or hemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted by the kidney in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production (erythropoiesis) in the bone marrow. Erythropoietin is an essential hormone for red blood cell production. EPO can cooperate with various other growth factors involved in the development of erythroid lineage from multipotent progenitors. To test the effect of EPO on cell proliferation, TF-1 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 5000 cells/well with 1% serum standard 1640 including various concentrations of recombinant human EPO. After incubated for 72h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10 microl of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37C. Proliferation of TF-1 cells after incubation with EPO for 72h observed by inverted microscope, and cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8 ) assay after incubation with recombinant EPO for 72h. EPO significantly increased cell viability of TF-1 cells.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2056
- Target nameEPO
- Target descriptionerythropoietin
- Target synonymsDBAL, ECYT5, EP, MVCD2, erythropoietin, epoetin
- Protein IDP01588
- Protein NameErythropoietin
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a secreted, glycosylated cytokine composed of four alpha helical bundles. The encoded protein is mainly synthesized in the kidney, secreted into the blood plasma, and binds to the erythropoietin receptor to promote red blood cell production, or erythropoiesis, in the bone marrow. Expression of this gene is upregulated under hypoxic conditions, in turn leading to increased erythropoiesis and enhanced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Expression of this gene has also been observed in brain and in the eye, and elevated expression levels have been observed in diabetic retinopathy and ocular hypertension. Recombinant forms of the encoded protein exhibit neuroprotective activity against a variety of potential brain injuries, as well as antiapoptotic functions in several tissue types, and have been used in the treatment of anemia and to enhance the efficacy of cancer therapies. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116124
- SpeciesHuman