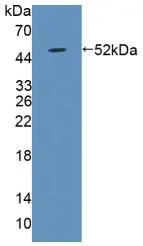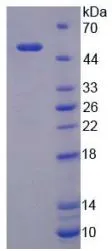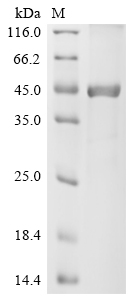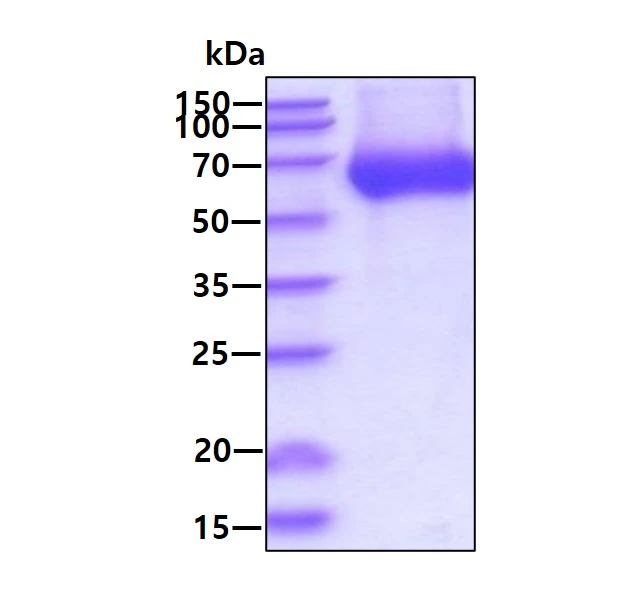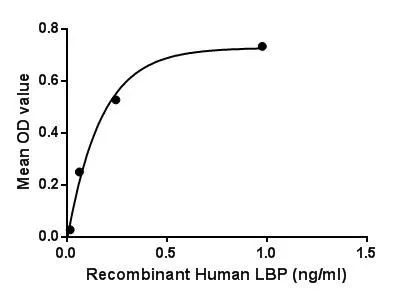
Functional ELISA analysis of GTX00248-pro Human LBP protein which can bind immobilized CD14 protein.
Human LBP protein, His tag
GTX00248-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP18428
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman LBP protein, His tag
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteLipopolysaccharide Binding Protein (LBP) is a soluble acute-phase protein that binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (or LPS) to elicit immune responses by presenting the LPS to important cell surface pattern recognition receptors called CD14 and TLR4. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the acute-phase immunologic response to gram-negative bacterial infections. This protein is part of a family of structurally and functionally related proteins, including BPI, plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), and phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP). Besides, Cluster Of Differentiation 14 (CD14) has been identified as an interactor of LBP, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human LBP and recombinant human CD14. Briefly, LBP were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to CD14-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-LBP pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of LBP and CD14 was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3929
- Target nameLBP
- Target descriptionlipopolysaccharide binding protein
- Target synonymsBPIFD2, lipopolysaccharide-binding protein, BPI fold containing family D, member 2, LPS-binding protein
- Protein IDP18428
- Protein NameLipopolysaccharide-binding protein
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is involved in the acute-phase immunologic response to gram-negative bacterial infections. Gram-negative bacteria contain a glycolipid, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), on their outer cell wall. Together with bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI), the encoded protein binds LPS and interacts with the CD14 receptor, probably playing a role in regulating LPS-dependent monocyte responses. Studies in mice suggest that the encoded protein is necessary for the rapid acute-phase response to LPS but not for the clearance of LPS from circulation. This protein is part of a family of structurally and functionally related proteins, including BPI, plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), and phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP). [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2012]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman