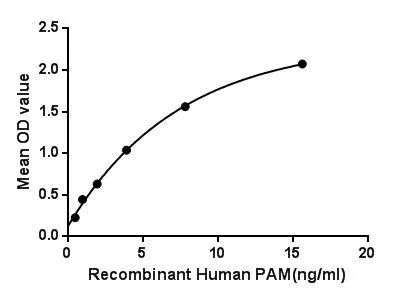
Functional ELISA analysis of GTX00180-pro Human PAM protein which can bind immobilized GaA protein.
Human PAM protein, His tag
GTX00180-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP19021
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman PAM protein, His tag
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NotePeptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is an enzyme that is required for the biosynthesis of many signaling peptides. This enzyme mainly includes two domains with distinct catalytic activities, a peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) domain and a peptidyl-alpha- hydroxyglycine alpha-amidating lyase (PAL) domain. These catalytic domains work sequentially to catalyze neuroendocrine peptides to active alpha-amidated products. Besides, Glucosidase Alpha, Acid (GaA) has been identified as an interactor of PAM, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human PAM and recombinant human GaA. Briefly, PAM were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to GaA-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-PAM pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of PAM and GaA was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5066
- Target namePAM
- Target descriptionpeptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase
- Target synonymsPAL, PAM-1, PHM, peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase, pancreatic peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase, peptidyl alpha-amidating enzyme, peptidyl-alpha-hydroxyglycine alpha-amidating lyase, peptidylamidoglycolate lyase, peptidylglycine 2-hydroxylase, peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase
- Protein IDP19021
- Protein NamePeptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a multifunctional protein. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature enzyme. This enzyme includes two domains with distinct catalytic activities, a peptidylglycine alpha-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) domain and a peptidyl-alpha-hydroxyglycine alpha-amidating lyase (PAL) domain. These catalytic domains work sequentially to catalyze the conversion of neuroendocrine peptides to active alpha-amidated products. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes an isoform that is proteolytically processed. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2016]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman