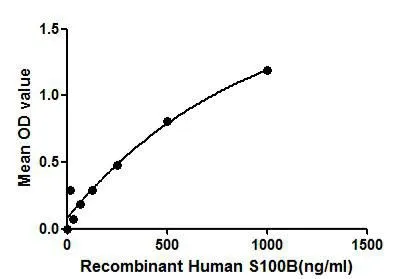
Functional ELISA analysis of GTX00117-pro Human S100 beta protein which can bind immobilized RAGE protein.
Human S100 beta protein, His tag
GTX00117-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP04271
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman S100 beta protein, His tag
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteProtein S100B is a member of the S100 family. S100 proteins are EF-hand calcium-binding proteins and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. Experimental results suggest that the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) plays important roles in mediating S100 protein-induced cellular signaling. Thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human S100B and recombinant human RAGE. Briefly, S100B were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to RAGE-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-S100B mAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of of S100B and RAGE was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6285
- Target nameS100B
- Target descriptionS100 calcium binding protein B
- Target synonymsNEF, S100, S100-B, S100beta, protein S100-B, S-100 calcium-binding protein, beta chain, S-100 protein subunit beta, S100 calcium-binding protein, beta (neural)
- Protein IDP04271
- Protein NameProtein S100-B
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21; however, this gene is located at 21q22.3. This protein may function in Neurite extension, proliferation of melanoma cells, stimulation of Ca2+ fluxes, inhibition of PKC-mediated phosphorylation, astrocytosis and axonal proliferation, and inhibition of microtubule assembly. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in several neurological, neoplastic, and other types of diseases, including Alzheimers disease, Downs syndrome, epilepsy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, melanoma, and type I diabetes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman