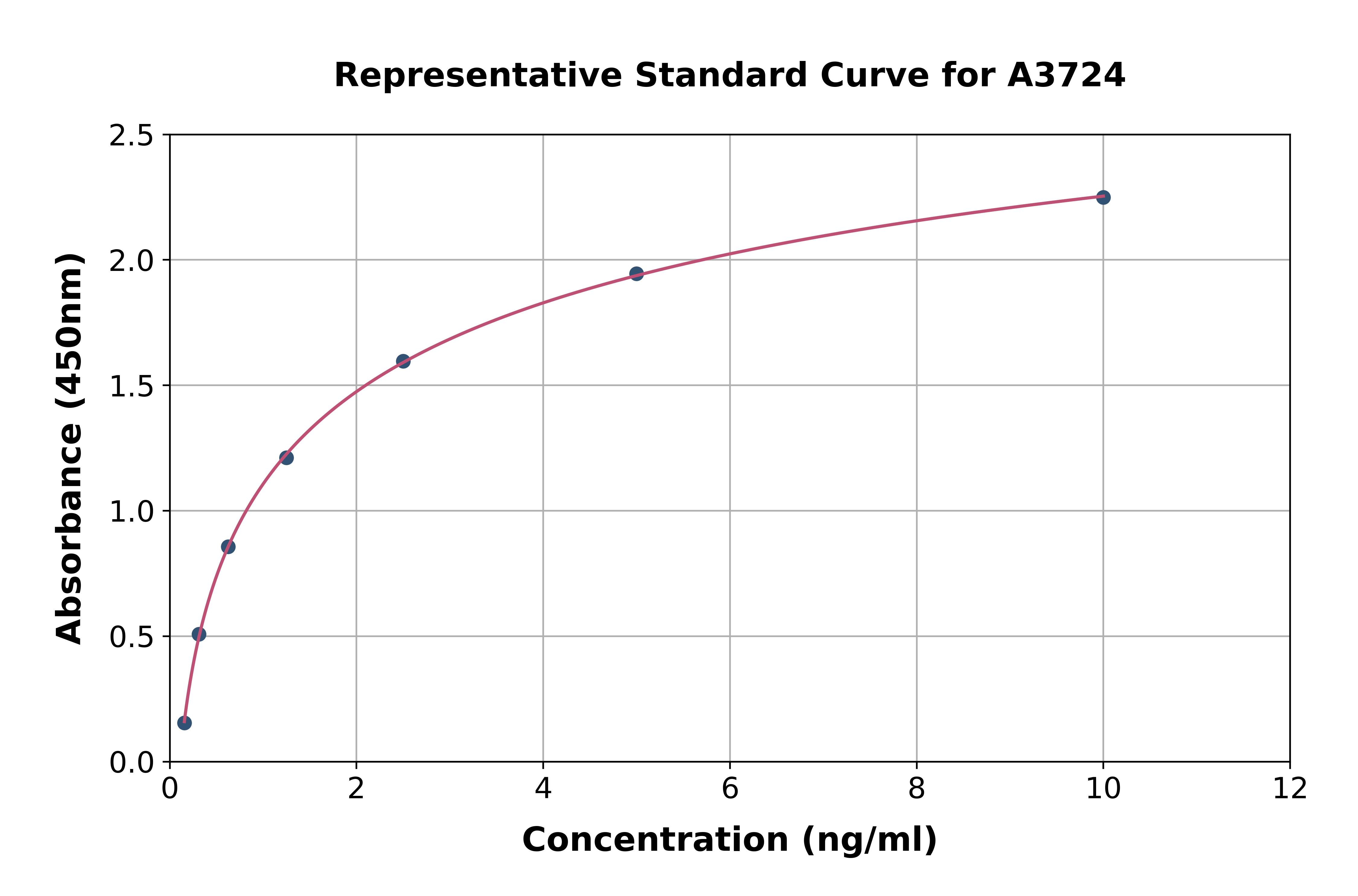
VEGF ELISA
BI-VEGF
Assay Sample Typeserum, EDTA plasma, citrate plasma, cc supernatants, urine
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierBiomedica
- Product NameVEGF ELISA
- Delivery Days Customer7
- ApplicationsELISA
- Applications SupplierELISA
- Assay Detection Range31.25-2000 pg/ml
- Assay Precisionintra-assay: 3%, inter-assay: 6%
- Assay Sample Typeserum, EDTA plasma, citrate plasma, cc supernatants, urine
- Assay Sensitivity15.6 pg/ml
- Assay Test PrincipleSandwich ELISA
- Assay Time4.5h
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Scientific DescriptionProduct Characteristics: The Biomedica VEGF Sandwich ELISA kit is a test that is intended for the quantitative measurement of VEGF levels in human serum and plasma samples. Target Information: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF or VEGF-A), is a growth hormone secreted by endothelial cells, fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, platelets, macrophages, and many other cell types. It belongs to the cysteine-knot growth factor superfamily (Peach C et al. ) and has a molecular weight of about 40 kDa. Up to date 17 different VEGF isoforms were described to be expressed from one single gene. They are produced by alternative promoter usage/initiation or alternative splicing/proteolysis after protein translation. The N-terminal region is responsible for receptor binding and conserved among all VEGF isoforms. In contrast, residues of the C-terminus differ between isoforms and determine protein length and properties: binding to co-receptor Neuropilin-1 (NRP1) or to extracellular matrix (ECM), agonist/antagonist of angiogenesis. Most isoforms result from the common transcripts: VEGF111, VEGF121, VEGF145, VEGF165, VEGF189 and VEGF206. Additionally, a third VEGF variant (VEGFAx), that demonstrates pro- and anti-apoptotic properties, was described. Thus, vascularization is tightly controlled by the balance of various splice variants, their availability and concentration, whereas isoforms linked to the ECM constitute a reservoir of VEGF that can quickly be shed to circulating forms (Peach C et al.). One of the most potent pro-angiogenic isoforms is VEGF165a. After secretion, 50-70% of VEGF165a is attached to the extracellular matrix (via heparin binding site), the rest is freely diffusible ( Peach C et al.). It is the most abundant isoform and enhances signaling over the VEGFR2 receptor by additionally binding to its co-receptor Neuropilin-1. VEGF A isoforms are glycosylated, homodimeric proteins. Two anti-parallel monomers are linked by intermolecular disulfide bonds (Wiesmann C et al.), whereas eight cysteine residues form a knot-like structure at one end of each monomer (Tjwa M et al.). However, heterodimerization with PLGF has been described as well (Olsson AK et al.).
- Storage Instruction2-8°C
- UNSPSC41116133