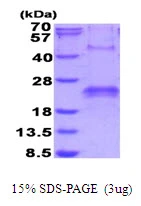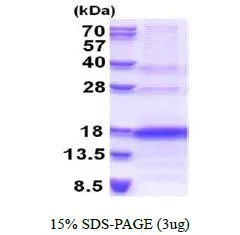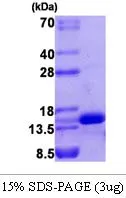
3 microg of GTX67186-pro Human VEGF121 protein (active) by SDS-PAGE under reducing condition and visualized by coomassie blue stain
Human VEGF121 protein (active)
GTX67186-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP15692
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman VEGF121 protein (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteMeasured in a cell proliferation assay using HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The ED50 for this effect is less or equal to 4 ng/ml.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Protein IDP15692
- Protein NameVascular endothelial growth factor A, long form
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family. It encodes a heparin-binding protein, which exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer. This growth factor induces proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, and is essential for both physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Disruption of this gene in mice resulted in abnormal embryonic blood vessel formation. This gene is upregulated in many known tumors and its expression is correlated with tumor stage and progression. Elevated levels of this protein are found in patients with POEMS syndrome, also known as Crow-Fukase syndrome. Allelic variants of this gene have been associated with microvascular complications of diabetes 1 (MVCD1) and atherosclerosis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. There is also evidence for alternative translation initiation from upstream non-AUG (CUG) codons resulting in additional isoforms. A recent study showed that a C-terminally extended isoform is produced by use of an alternative in-frame translation termination codon via a stop codon readthrough mechanism, and that this isoform is antiangiogenic. Expression of some isoforms derived from the AUG start codon is regulated by a small upstream open reading frame, which is located within an internal ribosome entry site. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2015]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352202