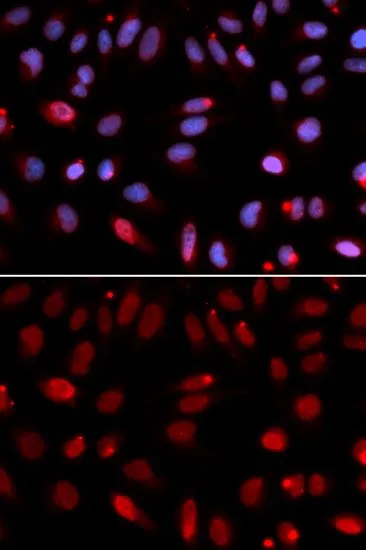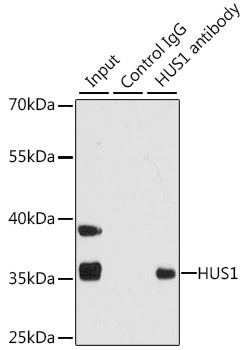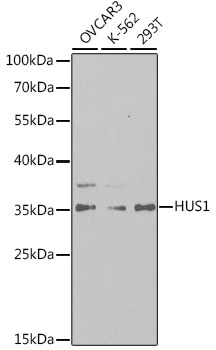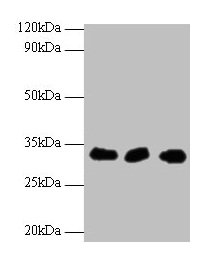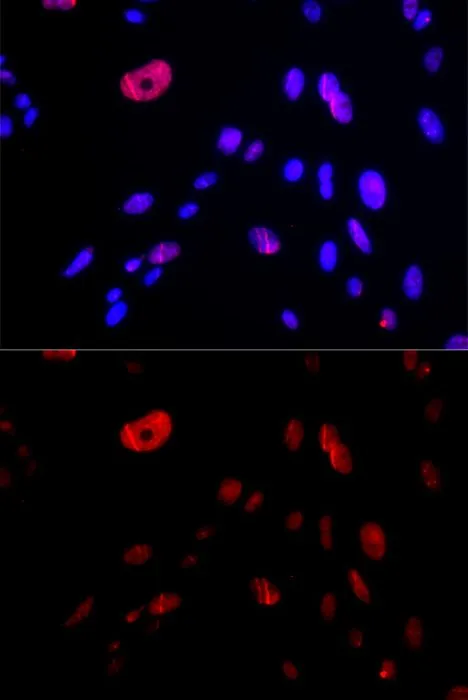
ICC/IF analysis of U2OS cells using GTX32662 HUS1 antibody. Blue : DAPI
HUS1 antibody
GTX32662
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHUS1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHUS1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
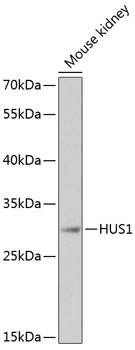
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:100. IP: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3364
- Target nameHUS1
- Target descriptionHUS1 checkpoint clamp component
- Target synonymshHUS1, checkpoint protein HUS1, HUS1 checkpoint homolog, hus1+-like protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO60921
- Protein NameCheckpoint protein HUS1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a component of an evolutionarily conserved, genotoxin-activated checkpoint complex that is involved in the cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. This protein forms a heterotrimeric complex with checkpoint proteins RAD9 and RAD1. In response to DNA damage, the trimeric complex interacts with another protein complex consisting of checkpoint protein RAD17 and four small subunits of the replication factor C (RFC), which loads the combined complex onto the chromatin. The DNA damage induced chromatin binding has been shown to depend on the activation of the checkpoint kinase ATM, and is thought to be an early checkpoint signaling event. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161