IL-1beta (human) ELISA Kit
AG-45B-0021
ReactivityHuman
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIL-1beta (human) ELISA Kit
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsELISA
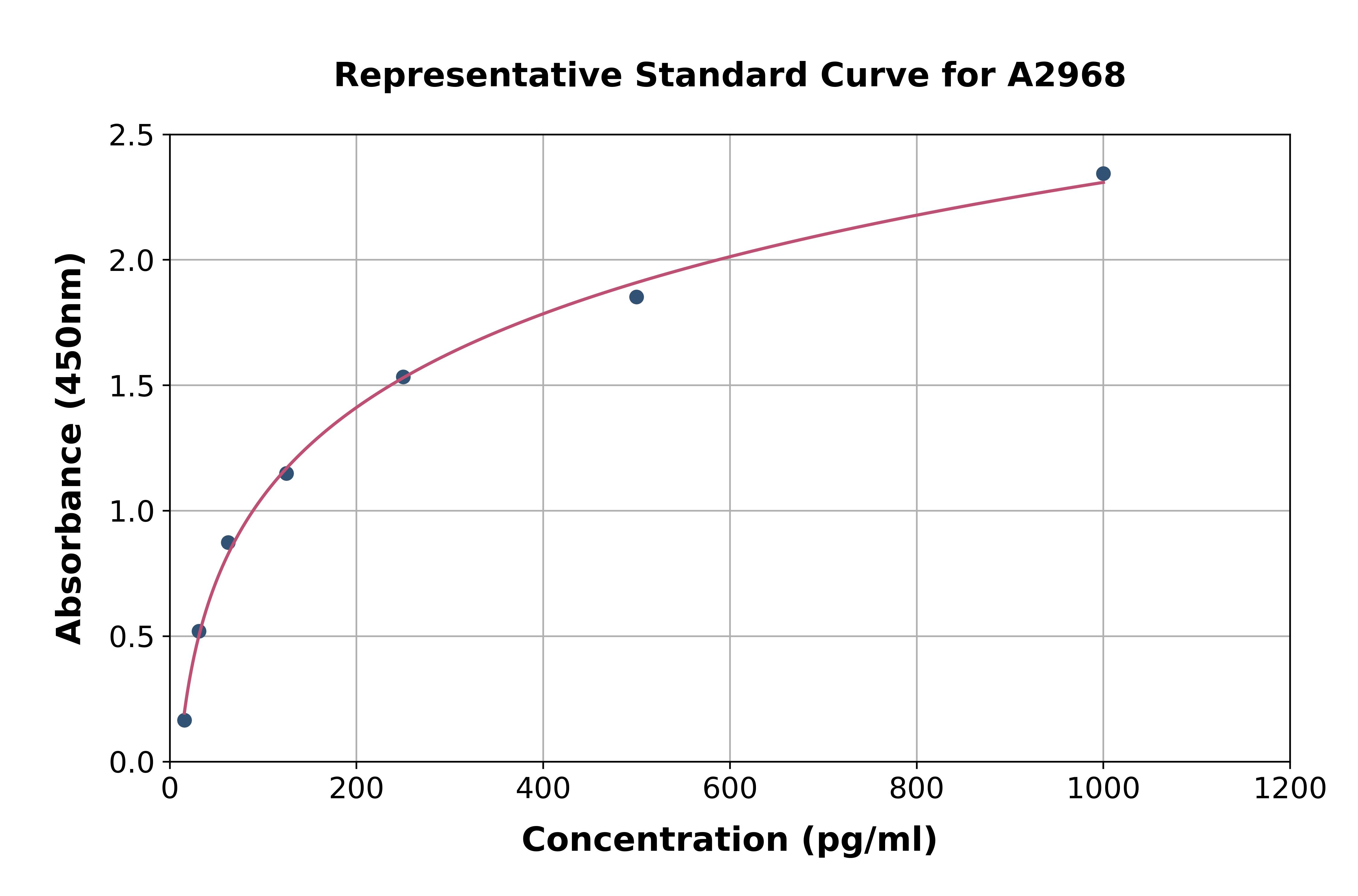
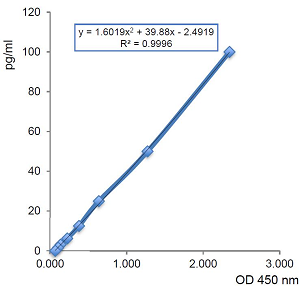
- Assay Detection Range1.5625 to 100pg/ml
- Assay Sensitivity0.7pg/ml
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Protein IDP01584
- Protein NameInterleukin-1 beta
- Scientific DescriptionColorimetric Sandwich ELISA Assay. Detects human IL-1beta in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatant. Range: 1.5625 to 100pg/ml. Sensitivity: 0.7pg/ml. The interleukin-1 (IL-1) family is a central mediator of innate immunity and inflammation. IL-1 family members are associated with both the development and progression of inflammatory diseases and have been linked to neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases. The IL-1 family of cytokines has 11 members, which are further subdivided into three groups, the IL-1, IL-18 and IL-36 subfamilies. The IL-1 cytokine subfamily includes agonists (IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and IL-33) as well as receptor antagonist IL-1Ra. IL-1beta and IL-1alpha exert similar biological effects acting on receptor IL-1R, eliciting pro-inflammatory actions. Unlike IL-1alpha which is both constitutively expressed and active in its 31kDa pro-form, IL-1beta is only produced in its inactive 35kDa pro-form following priming signals, such as pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs) and is subsequently cleaved to its 17kDa active form following inflammasome activation in damaged or diseased states. IL-1beta is expressed by activated macrophages and monocytes. Active IL-1beta has known roles in initiating and propagating sterile inflammation, including macrophage recruitment, activation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) and modulating chemokine expression. IL-1beta, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes play important roles in several diseases such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis, neuronal injuries, such as Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, stroke, cerebral ischemic cell death, multiple sclerosis and Down syndrome. Some human hereditary or acquired diseases have been linked to elevated IL-1beta such as cryopyrin-associated periodic syndroms (CAPS) directly linked to NLRP3 mutations. - The interleukin-1 (IL-1) family is a central mediator of innate immunity and inflammation. IL-1 family members are associated with both the development and progression of inflammatory diseases and have been linked to neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases. The IL-1 family of cytokines has 11 members, which are further subdivided into three groups, the IL-1, IL-18 and IL-36 subfamilies. The IL-1 cytokine subfamily includes agonists (IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and IL-33) as well as receptor antagonist IL-1Ra. IL-1beta and IL-1alpha exert similar biological effects acting on receptor IL-1R, eliciting pro-inflammatory actions. Unlike IL-1alpha which is both constitutively expressed and active in its 31kDa pro-form, IL-1beta is only produced in its inactive 35kDa pro-form following priming signals, such as pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs or DAMPs) and is subsequently cleaved to its 17kDa active form following inflammasome activation in damaged or diseased states. IL-1beta is expressed by activated macrophages and monocytes. Active IL-1beta has known roles in initiating and propagating sterile inflammation, including macrophage recruitment, activation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) and modulating chemokine expression. IL-1beta, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes play important roles in several diseases such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atherosclerosis, neuronal injuries, such as Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, stroke, cerebral ischemic cell death, multiple sclerosis and Down syndrome. Some human hereditary or acquired diseases have been linked to elevated IL-1beta such as cryopyrin-associated periodic syndroms (CAPS) directly linked to NLRP3 mutations.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman