IL-22 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (non-lytic)
AG-40B-0230
Protein IDQ9GZX6
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIL-22 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (non-lytic)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
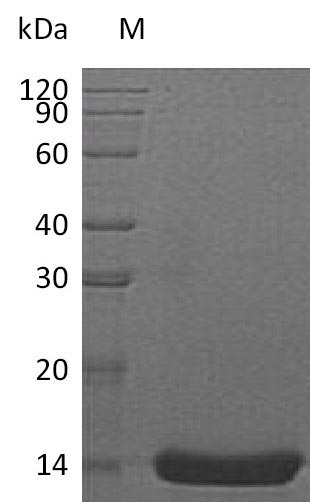
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID50616
- Target nameIL22
- Target descriptioninterleukin 22
- Target synonymsIL-21, IL-22, IL-D110, IL-TIF, ILTIF, TIFIL-23, TIFa, zcyto18, interleukin-22, IL-10-related T-cell-derived inducible factor, cytokine Zcyto18
- Protein IDQ9GZX6
- Protein NameInterleukin-22
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Protein. Extracellular domain of human IL-22 (aa 34-179) is fused to the N-terminus of the human Fc IgG1 (non-lytic mutant). Source: W2. Lyophilized. Contains PBS. The IL-22 gene includes five exons and a 537 bp-long open reading frame that encodes for a 179 amino acid protein. IL-22 is a member of the IL-10 family of cytokines, which also includes IL-19, -20, -24, and -26, IL-28A/B, and IL-29 and IFNlambda. Mouse and human IL-22 share 79% homology. IL-22 is mainly produced by lymphocytes, such as T helper type 1 (Th1), Th17, Th22, CD8+ T cells, gammadelta T cells, natural killer cells, lymphoid tissue inducer cells, innate lymphoid type 3 (ILC3) cells, and also by neutrophils. IL-22 has two heterodimeric transmembrane receptors, IL-22R1 and IL-10R2, which subsequently activate the JAK/STAT3, ERK and JNK pathways. IL-22 responsiveness is limited by epithelial cell-restricted expression of IL-22RA1 in the lung, gastrointestinal tract, thymus, skin, pancreas, liver, and kidney and represents a major communication channel between the immune system and specialized tissue cell types. IL-22 is a critical regulator of epithelial homeostasis, implicated in multiple aspects of epithelial barrier function, including regulation of epithelial cell growth and permeability, production of mucus and antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) and complement production. IL-22 plays key functions in the intestine and, therefore, plays a protective role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IL-22 is also a controversial cytokine in tumor development; the IL-22-STAT3 axis induces anti-apoptotic genes and provides survival and proliferation signals for both normal and malignant cells. Therefore, in healthy conditions, it prevents tumor formation; however, once a tumor has been established, IL-22 promotes tumorigenesis. - The IL-22 gene includes five exons and a 537 bp-long open reading frame that encodes for a 179 amino acid protein. IL-22 is a member of the IL-10 family of cytokines, which also includes IL-19, -20, -24, and -26, IL-28A/B, and IL-29 and IFNlambda. Mouse and human IL-22 share 79% homology. IL-22 is mainly produced by lymphocytes, such as T helper type 1 (Th1), Th17, Th22, CD8+ T cells, gammadelta T cells, natural killer cells, lymphoid tissue inducer cells, innate lymphoid type 3 (ILC3) cells, and also by neutrophils. IL-22 has two heterodimeric transmembrane receptors, IL-22R1 and IL-10R2, which subsequently activate the JAK/STAT3, ERK and JNK pathways. IL-22 responsiveness is limited by epithelial cell-restricted expression of IL-22RA1 in the lung, gastrointestinal tract, thymus, skin, pancreas, liver, and kidney and represents a major communication channel between the immune system and specialized tissue cell types. IL-22 is a critical regulator of epithelial homeostasis, implicated in multiple aspects of epithelial barrier function, including regulation of epithelial cell growth and permeability, production of mucus and antimicrobial proteins (AMPs) and complement production. IL-22 plays key functions in the intestine and, therefore, plays a protective role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). IL-22 is also a controversial cytokine in tumor development; the IL-22-STAT3 axis induces anti-apoptotic genes and provides survival and proliferation signals for both normal and malignant cells. Therefore, in healthy conditions, it prevents tumor formation; however, once a tumor has been established, IL-22 promotes tumorigenesis.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesHuman