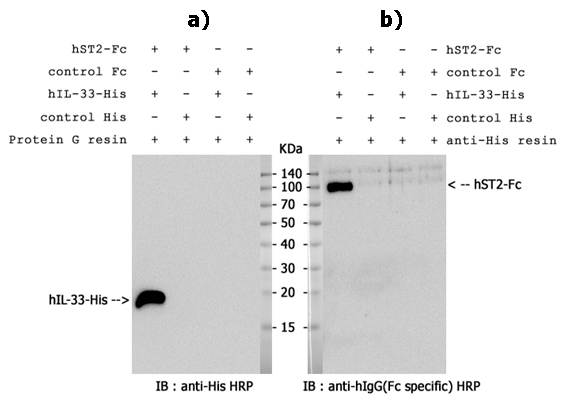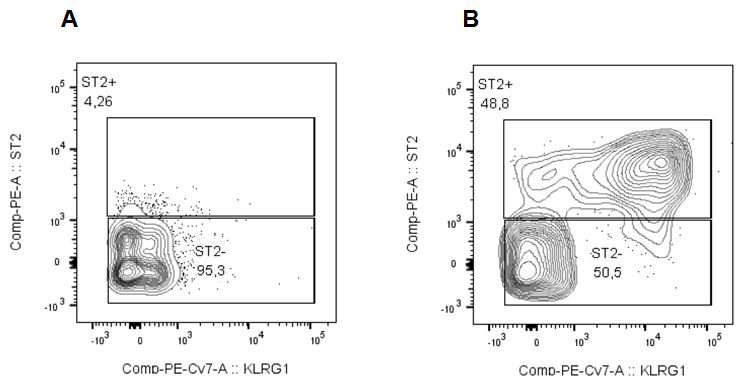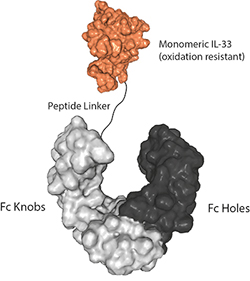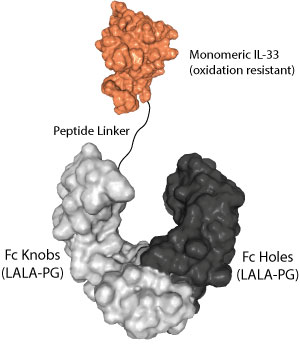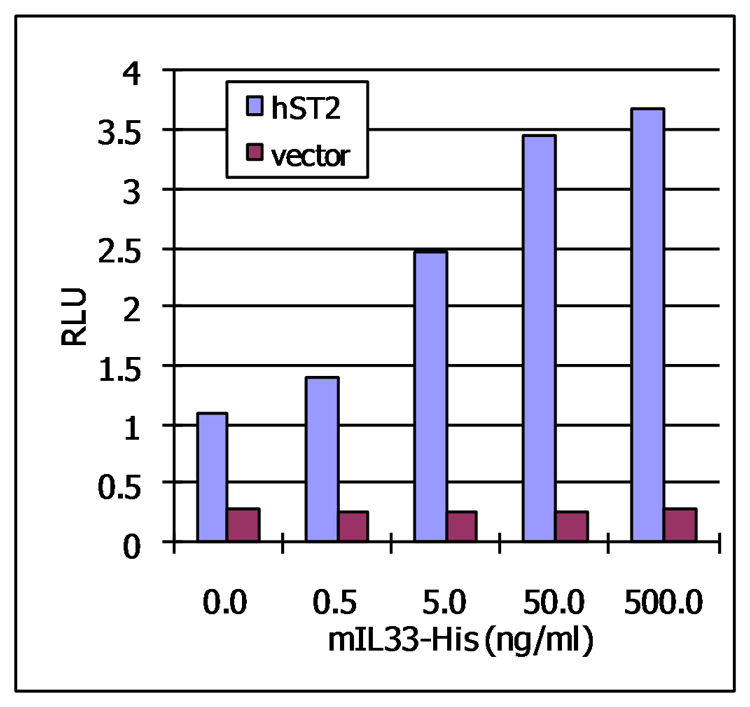
Activation of a human ST2-dependent NF-kappaB pathway. HEK-293 cells were transiently co-transfected with 500 ng of human ST2-containing vector (or empty vector as a negative control), a vector containing NF-kappaB-driven firefly luciferase, and
IL-33 (mouse) (rec.) (His)
AG-40A-0053
Protein IDQ2YEJ4
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIL-33 (mouse) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID77125
- Target nameIl33
- Target descriptioninterleukin 33
- Target synonyms9230117N10Rik, Il-33, Il1f11, NF-HEV, interleukin-33, nuclear factor from high endothelial venules
- Protein IDQ2YEJ4
- Protein NameInterleukin-33
- Scientific DescriptionInterleukin-33 (IL-33; HF-NEV; IL-1F11), a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, is expressed by many cell types following pro-inflammatory stimulation and is thought to be released on cell lysis. The 30kDa human IL33 is converted by CASP1 to a 18kDa protein. IL33 binds to and signals through ST2 (IL1R1) and its stimulation recruits MYD88, IRAK, IRAK4, and TRAF6, followed by phosphorylation of ERK1 (MAPK3)/ERK2 (MAPK1), p38 (MAPK14), and JNK. The ability of IL-33 to target numerous immune cell types, like Th2-like cells, mast cells, and B1 cells, and to induce cytokine and chemokine production underlines its potential in influencing the outcome of a wide range of diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, atopic allergy & anaphylaxis, cardiovascular disease/atherosclerosis, nervous system diseases, and sepsis. - Protein. Mouse IL-33 (aa 109-266) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Source: E. coli. Endotoxin content: 90% (SDS-PAGE). Interleukin-33 (IL-33; HF-NEV; IL-1F11), a member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, is expressed by many cell types following pro-inflammatory stimulation and is thought to be released on cell lysis. The 30kDa human IL33 is converted by CASP1 to a 18kDa protein. IL33 binds to and signals through ST2 (IL1R1) and its stimulation recruits MYD88, IRAK, IRAK4, and TRAF6, followed by phosphorylation of ERK1 (MAPK3)/ERK2 (MAPK1), p38 (MAPK14), and JNK. The ability of IL-33 to target numerous immune cell types, like Th2-like cells, mast cells, and B1 cells, and to induce cytokine and chemokine production underlines its potential in influencing the outcome of a wide range of diseases, such as arthritis, asthma, atopic allergy & anaphylaxis, cardiovascular disease/atherosclerosis, nervous system diseases, and sepsis.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesMouse