IL-7 (human) (rec.) (His)
CHI-HF-20107
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierChimerigen Laboratories
- Product NameIL-7 (human) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
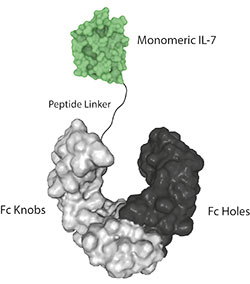
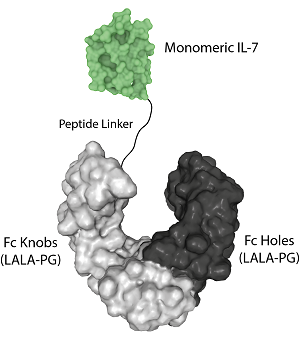
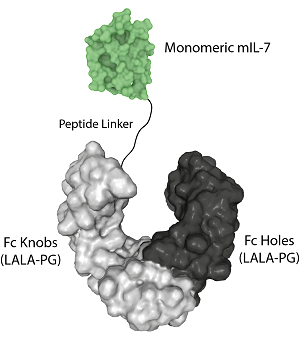
- Scientific DescriptionInterleukin-7 (IL-7), is a hematopoietic growth factor and a member of the IL-7/IL-9 family. IL-7 stimulates the proliferation of lymphoid progenitors and is secreted by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. IL-7 is also important for proliferation during certain stages of B cell maturation. IL-7 and the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) form a heterodimer that functions as a pre-pro-B cell growth-stimulating factor. It is found to be a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta (TCRbeta) during early T cell development. IL-7 can be produced locally by intestinal epithelial and epithelial goblet cells and may serve as a regulatory factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes. - Protein. The extracellular domain of human IL-7 (aa 26-177) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Source: HEK 293 cells. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). Interleukin-7 (IL-7), is a hematopoietic growth factor and a member of the IL-7/IL-9 family. IL-7 stimulates the proliferation of lymphoid progenitors and is secreted by stromal cells in the bone marrow and thymus. IL-7 is also important for proliferation during certain stages of B cell maturation. IL-7 and the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) form a heterodimer that functions as a pre-pro-B cell growth-stimulating factor. It is found to be a cofactor for V(D)J rearrangement of the T cell receptor beta (TCRbeta) during early T cell development. IL-7 can be produced locally by intestinal epithelial and epithelial goblet cells and may serve as a regulatory factor for intestinal mucosal lymphocytes.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesHuman