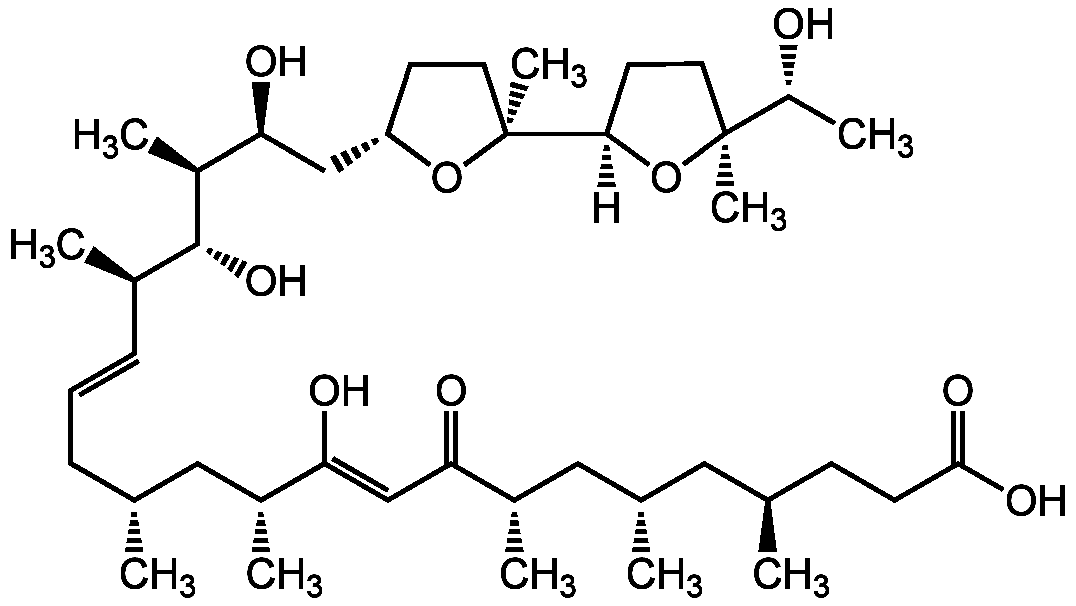
Chemical Structure
Ionomycin (free acid) [56092-81-0]
AG-CN2-0416
CAS Number56092-81-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight709
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIonomycin (free acid) [56092-81-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number56092-81-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC41H72O9
- Molecular Weight709
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic [1]. Potent and highly selective Ca2+ ionophore. Commonly used to modify intracellular calcium levels to study calcium transport across biological membranes and to calibrate fluorescent Ca2+ indicators [2, 3]. Ionomycin also transports Pb2+ and some other divalent cations, as well as several lanthanide series trivalent cations at efficiencies that are greater than or equal to those for Ca2+ [3, 9]. Apoptosis inducer [4, 7]. Induces apoptotic neuronal degeneration in embryonic cortical neurons and cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and induces central demyelination [6]. Used to stimulate the intracellular production of the cytokines, interferon, perforin, IL-2 and IL-4 usually in conjunction with PMA [5, 8]. ADAM10 agonist [10]. Potent inducer of shedding CXCL16 [10]. TREK-1 channels inhibitor [11]. PPARgamma ligand with a unique binding mode. Shows effective glucose-lowering activity in a mouse model of diabetes [12]. - Chemical. CAS: 56092-81-0. Formula: C41H72O9. MW: 709. Isolated from Streptomyces conglobatus. Antibiotic. Potent and highly selective Ca2+ ionophore. Commonly used to modify intracellular calcium levels to study calcium transport across biological membranes and to calibrate fluorescent Ca2+ indicators. Ionomycin also transports Pb2+ and some other divalent cations, as well as several lanthanide series trivalent cations at efficiencies that are greater than or equal to those for Ca2+. Apoptosis inducer. Induces apoptotic neuronal degeneration in embryonic cortical neurons and cell cycle arrest at G1 phase and induces central demyelination. Used to stimulate the intracellular production of the cytokines, interferon, perforin, IL-2 and IL-4 usually in conjunction with PMA. ADAM10 agonist. Potent inducer of shedding CXCL16. TREK-1 channels inhibitor. PPARgamma ligand with a unique binding mode. Shows effective glucose-lowering activity in a mouse model of diabetes.
- SMILES[H][C@@]1(CC[C@](C)(O1)[C@@H](C)O)[C@]1(C)CC[C@@H](C[C@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)\C=C\C[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C(\O)=C\C(=O)[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](C)C[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200



![Ionomycin [56092-81-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/38/00/CgoaEGayVNqEIXy4AAAAAHs1XHo301.png)