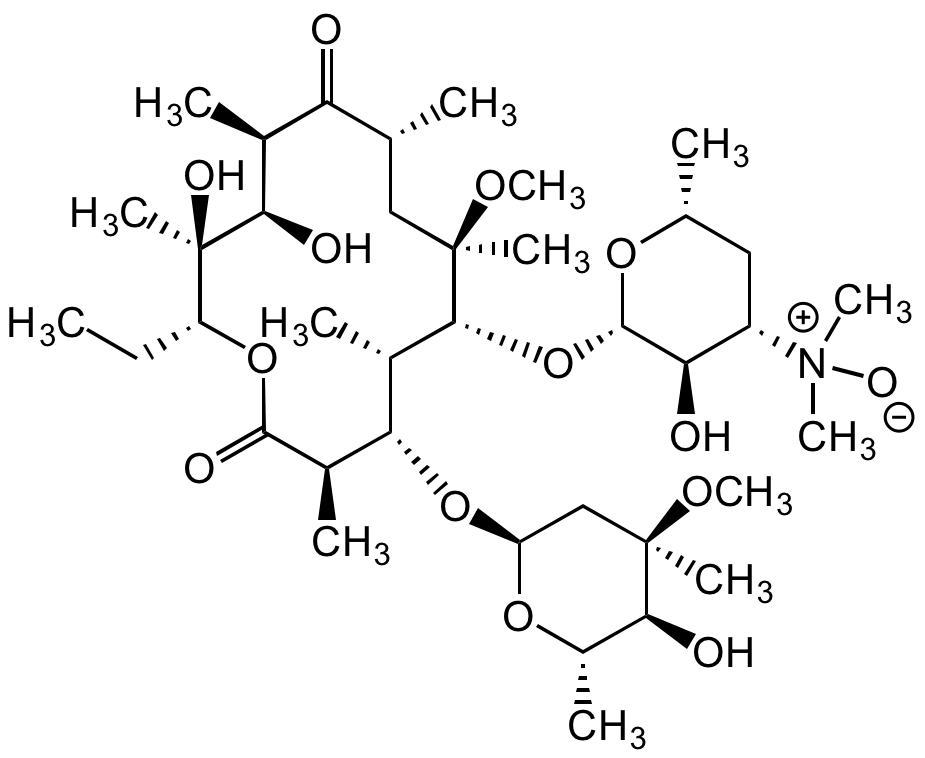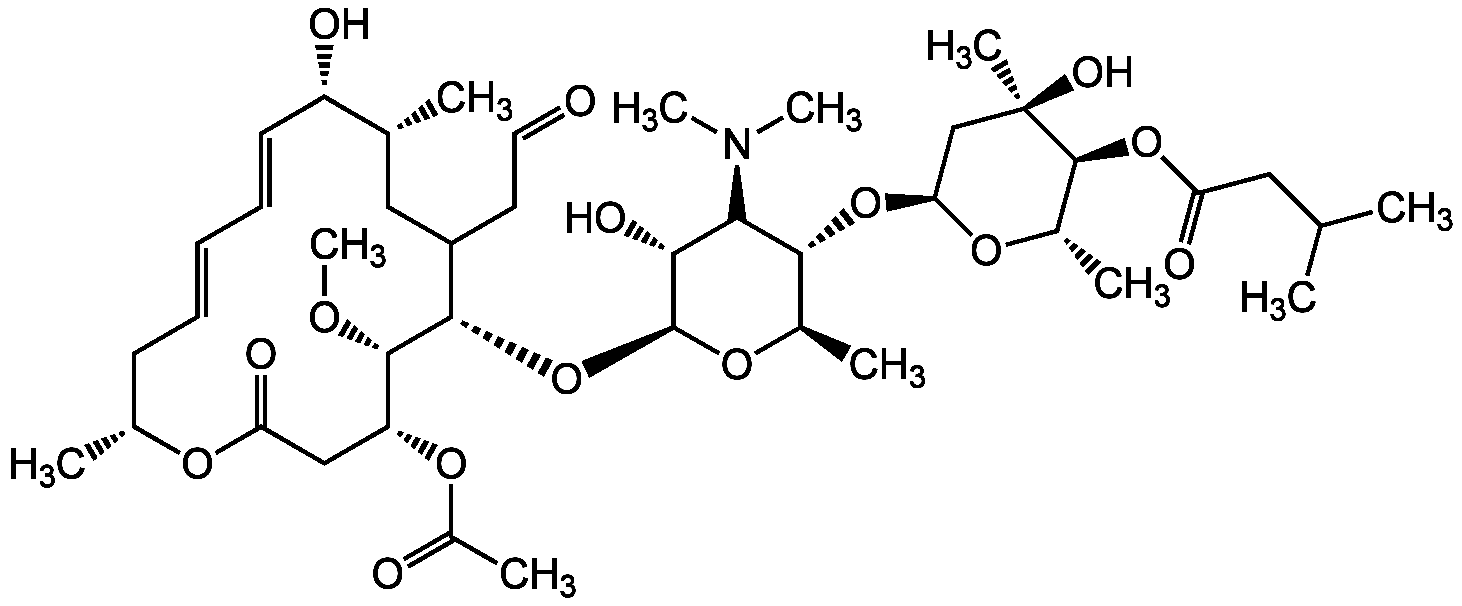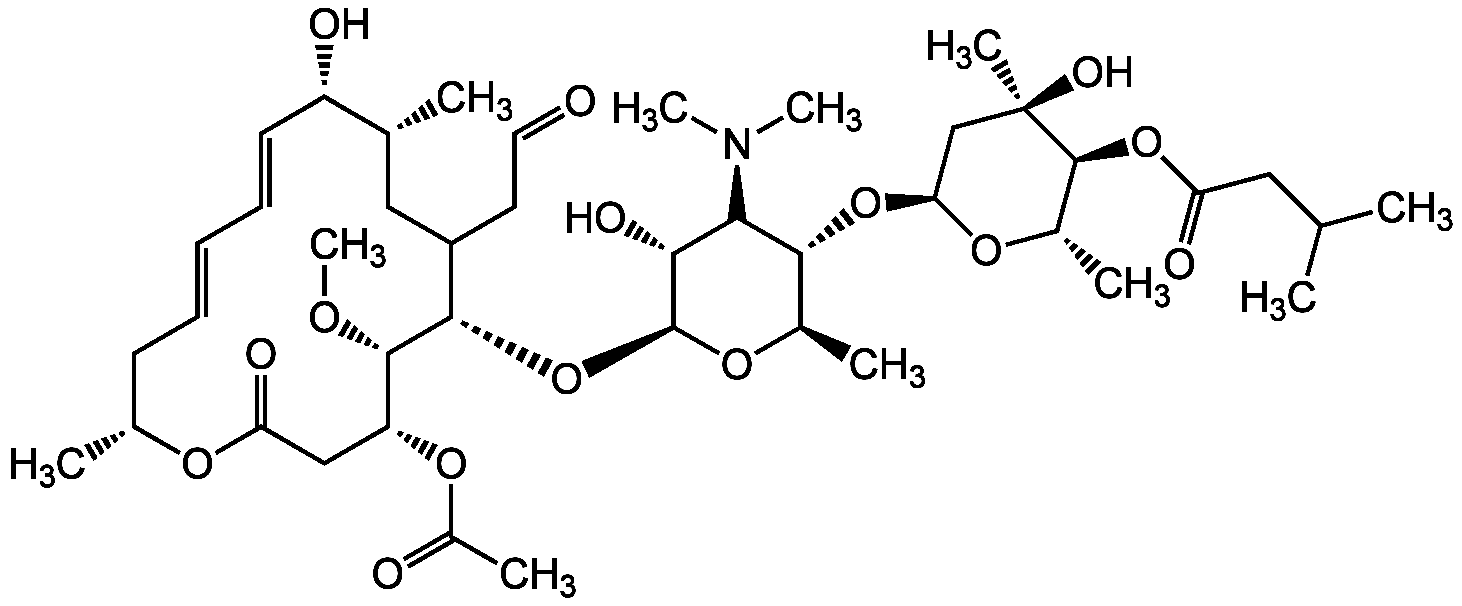
Chemical Structure
Josamycin Solution, 10 ug/ml in acetone
CDX-J0009
CAS Number16846-24-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight827.99
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameJosamycin Solution, 10 ug/ml in acetone
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number16846-24-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration10 ug/ml
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC42H69NO15
- Molecular Weight827.99
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 16846-24-5. Formula: C42H69NO15. MW: 827.99. Josamycin is a member of the leucomycin family of macrolide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces kitasatoensis. It is an antimicrobial against a wide variety of pathogens. It has activity against Gram-positive an Gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action is via inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly to the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting peptidyltransferase and ribosomal translocation, thereby inhibiting translocation of peptidyl tRNA. Josamycin may overcome anticancer drug resistance by inhibiting the binding of vinblastine or cyclosporin A to P-glycoprotein (Pgp). It is used to study the modification of phagocytosis and cytokine production by macrolide antibiotics and immunomodulatory effects. - Josamycin is a member of the leucomycin family of macrolide antibiotics produced by Streptomyces kitasatoensis. It is an antimicrobial against a wide variety of pathogens. It has activity against Gram-positive an Gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action is via inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly to the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, inhibiting peptidyltransferase and ribosomal translocation, thereby inhibiting translocation of peptidyl tRNA. Josamycin may overcome anticancer drug resistance by inhibiting the binding of vinblastine or cyclosporin A to P-glycoprotein (Pgp). It is used to study the modification of phagocytosis and cytokine production by macrolide antibiotics and immunomodulatory effects.
- SMILESO=C1O[C@H](C)C/C=C/C=C/[C@H](O)[C@H](C)CC(CC=O)[C@H](O[C@@H]2O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@H]3O[C@@H](C)[C@H](OC(CC(C)C)=O)[C@](C)(O)C3)[C@@H](N(C)C)[C@H]2O)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC(C)=O)C1
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UN Number1090
- UNSPSC12352200


![JOSAMYCIN [16846-24-5]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/88/CgoaEWayI6yETk4VAAAAANUfPGM544.png)