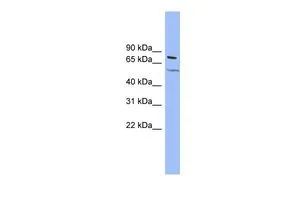
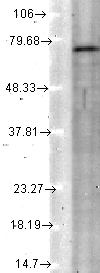
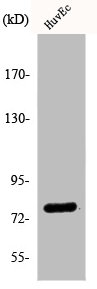WB analysis of cerebellum lysate using GTX88722 KCNQ4 antibody, Internal. Dilution : 2μg/ml Loading : 35μg protein in RIPA buffer
KCNQ4 antibody, Internal
GTX88722
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetKCNQ4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKCNQ4 antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-3microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9132
- Target nameKCNQ4
- Target descriptionpotassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 4
- Target synonymsDFNA2, DFNA2A, KV7.4, potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4, potassium channel KQT-like 4, potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT4, potassium channel, voltage gated KQT-like subfamily Q, member 4, potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 4
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP56696
- Protein NamePotassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene forms a potassium channel that is thought to play a critical role in the regulation of neuronal excitability, particularly in sensory cells of the cochlea. The current generated by this channel is inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. The encoded protein can form a homomultimeric potassium channel or possibly a heteromultimeric channel in association with the protein encoded by the KCNQ3 gene. Defects in this gene are a cause of nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness type 2 (DFNA2), an autosomal dominant form of progressive hearing loss. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161