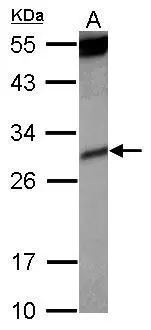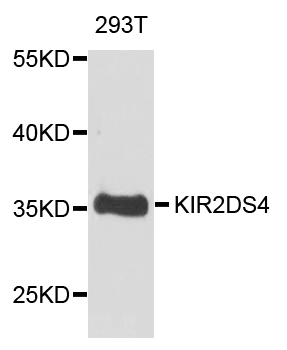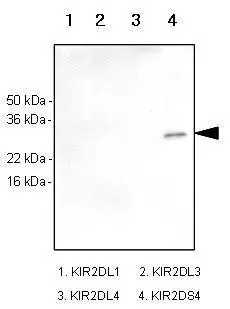
Recombinant human kIR2DL1, kIR2DL3, kIR2DL4 and kIR2DS4 (each 100ng) were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane and probed with anti-human kIR2DS4 antibody (1:1,000). Proteins were visualized using a goat anti-mouse secondary antibody conjuga
KIR2DS4 antibody [5F2]
GTX50069
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetKIR2DS4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKIR2DS4 antibody [5F2]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWe recommend the following starting dilutions:Western Blot: Use at 1:500 ~ 2,000.Optimal working concentrations should be determined experimentally by the end user.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID5F2
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3809
- Target nameKIR2DS4
- Target descriptionkiller cell immunoglobulin like receptor, two Ig domains and short cytoplasmic tail 4 (gene/pseudogene)
- Target synonymsCD158I, KIR-2DS4, KIR1D, KIR412, KKA3, NKAT-8, NKAT8, killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS4, CD158 antigen-like family member I, KIR antigen 2DS4, P58 natural killer cell receptor clones CL-39/CL-17, killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, two domains, short cytoplasmic tail, 4, killer inhibitory receptor 4-1-2, natural killer-associated transcript 8, p50 killer cell activating receptor KAR-K1d, p58 NK receptor CL-39/CL-17
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP43632
- Protein NameKiller cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS4
- Scientific DescriptionKiller cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several framework genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203



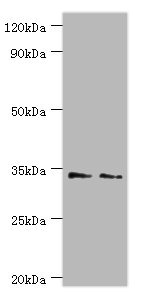
![WB analysis of HEK293 expressing human KIR2DS4 using GTX52897 KIR2DS4 antibody [2G42].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX52897/GTX52897_20191119_WB_w_23060900_292.webp)