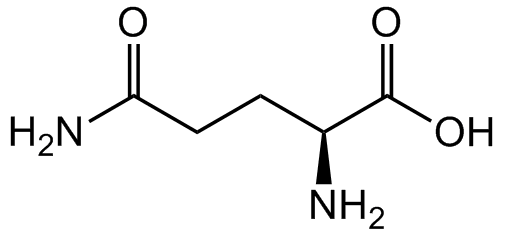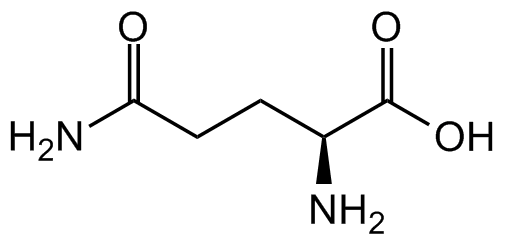
Chemical Structure
L-Glutamine [56-85-9] [56-85-9]
CDX-G0041
CAS Number56-85-9
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight146.14
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameL-Glutamine [56-85-9] [56-85-9]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number56-85-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Molecular FormulaC5H10N2O3
- Molecular Weight146.14
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 56-85-9. Formula: C5H10N2O3. MW: 146.14. L-Glutamine is an amino acid and is essential in the formation of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, amino sugars, glutathione, L-glutamate and other amino acids as well as in protein synthesis and glucose production. It plays also a role in lipid synthesis (e.g. in cancer cells), cellular energy as a source next to glucose, nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines and carbon donation, as a source refilling the citric acid cycle. It is a nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation and a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate and GABA. L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid which is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, next to its roles in cell proliferation and cancer. Levels of L-glutamine in human white adipose tissue (WAT) are linked with obesity-associated inflammation. Addition of L-glutamine in obese mice attenuated adipose tissue inflammation. Reduced L-glutamine levels during obesity shift the balance from glutaminolysis toward glycolysis, leading to nuclear O-GlcNAcylation, which activates inflammation. - L-Glutamine is an amino acid and is essential in the formation of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides, amino sugars, glutathione, L-glutamate and other amino acids as well as in protein synthesis and glucose production. It plays also a role in lipid synthesis (e.g. in cancer cells), cellular energy as a source next to glucose, nitrogen donation for many anabolic processes, including the synthesis of purines and carbon donation, as a source refilling the citric acid cycle. It is a nontoxic transporter of ammonia in the blood circulation and a precursor to the neurotransmitter glutamate and GABA. L-Glutamine is an essential amino acid which is a crucial component of culture media that serves as a major energy source for cells in culture. L-Glutamine exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, next to its roles in cell proliferation and cancer. Levels of L-glutamine in human white adipose tissue (WAT) are linked with obesity-associated inflammation. Addition of L-glutamine in obese mice attenuated adipose tissue inflammation. Reduced L-glutamine levels during obesity shift the balance from glutaminolysis toward glycolysis, leading to nuclear O-GlcNAcylation, which activates inflammation.
- SMILESNC(CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200