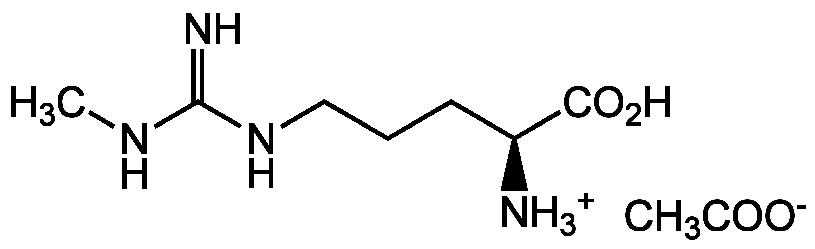
Chemical Structure
L-NMMA . monoacetate [53308-83-1] [53308-83-1]
AG-CR1-3578
CAS Number53308-83-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>99%
Molecular Weight188.2 . 60.1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameL-NMMA . monoacetate [53308-83-1] [53308-83-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number53308-83-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Molecular FormulaC7H16N4O2 . CH3COOH
- Molecular Weight188.2 . 60.1
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 53308-83-1. Formula: C7H16N4O2 . CH3COOH. MW: 188.2 . 60.1. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibitor. Inhibits the generation of NO from arginine. Competitive, irreversible non-selective inhibitor of all three NOS I, II, and III isoforms (eNOS, iNOS and nNOS). Inhibits the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) in a dose-dependent and enantiospecific fashion. Useful tool to study the role and the effects of NO in cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disorders, hypertension, diabetes, septic shock, inflammation, infection, stroke and neurodegenerative disorders. - Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibitor. Inhibits the generation of NO from arginine. Competitive, irreversible non-selective inhibitor of all three NOS I, II, and III isoforms (eNOS, iNOS and nNOS). Inhibits the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) in a dose-dependent and enantiospecific fashion. Useful tool to study the role and the effects of NO in cardiovascular and gastrointestinal disorders, hypertension, diabetes, septic shock, inflammation, infection, stroke and neurodegenerative disorders.
- SMILESCC([O-])=O.CNC(=N)NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![L-NMMA acetate [53308-83-1] [53308-83-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/6D/CgoaEWayH2eETdAoAAAAAO0D4GI822.png)