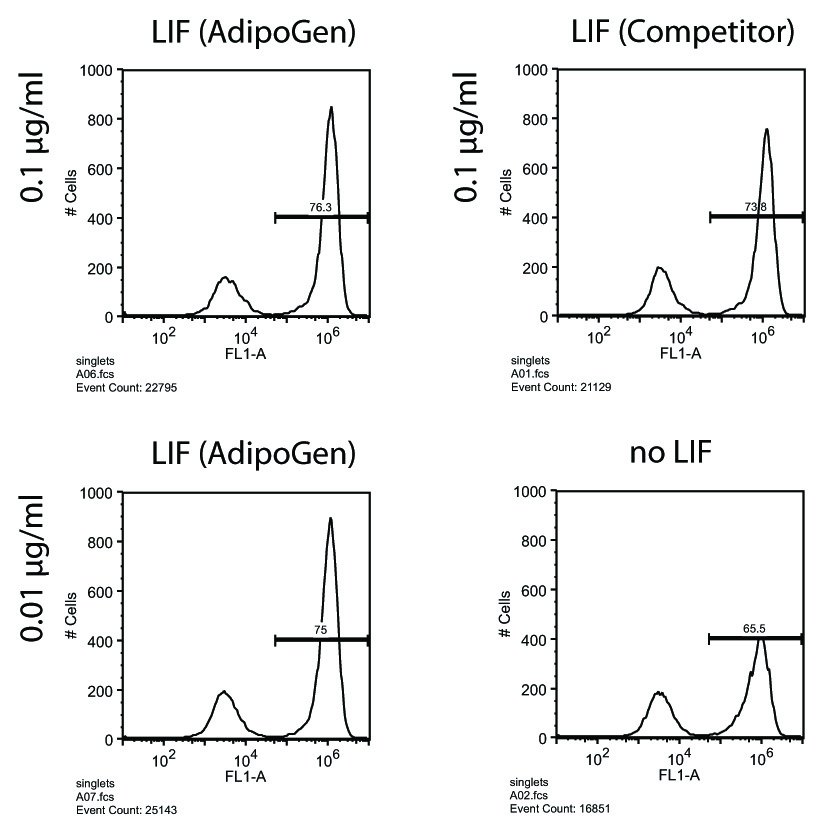
Figure: Human Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) (rec.) (AG-40B-0093) maintains pluripotency of mouse ES cells. Method: Mouse ES oct4 GFP cells were cultured for 3 days in the presence of the indicated concentrations of LIF and followed
LIF (human) (rec.)
AG-40B-0093
Protein IDP15018
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameLIF (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID3976
- Target nameLIF
- Target descriptionLIF interleukin 6 family cytokine
- Target synonymsCDF, DIA, HILDA, MLPLI, leukemia inhibitory factor, D factor, cholinergic differentiation factor, differentiation inhibitory activity, differentiation-inducing factor, differentiation-stimulating factor, hepatocyte-stimulating factor III, human interleukin in DA cells, melanoma-derived LPL inhibitor
- Protein IDP15018
- Protein NameLeukemia inhibitory factor
- Scientific DescriptionLIF has the capacity to induce terminal differentiation in leukemic cells. Its activities also include the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, the induction of neuronal cell differentiation and the stimulation of acute-phase protein synthesis in hepatocytes. LIF activates JAK & STAT signaling in human embryonic stem (ES) cells, but this pathway does not maintain pluripotency in these cells, which instead rely on FGF2-mediated ERK signaling. By contrast, mouse ES cells can be maintained by LIF-mediated JAK & STAT signaling. LIF binds to a high affinity heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of two proteins: LIF-R alpha that binds LIF with low affinity and the 130kDa (gp130) subunit that by itself does not bind LIF, but is required for high affinity binding of LIF. - Protein. Human LIF (aa 23-202) is fused at the N-terminus to a tag. Source: E. coli. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). LIF has the capacity to induce terminal differentiation in leukemic cells. Its activities also include the induction of hematopoietic differentiation in normal and myeloid leukemia cells, the induction of neuronal cell differentiation and the stimulation of acute-phase protein synthesis in hepatocytes. LIF activates JAK & STAT signaling in human embryonic stem (ES) cells, but this pathway does not maintain pluripotency in these cells, which instead rely on FGF2-mediated ERK signaling. By contrast, mouse ES cells can be maintained by LIF-mediated JAK & STAT signaling. LIF binds to a high affinity heterodimeric receptor complex consisting of two proteins: LIF-R alpha that binds LIF with low affinity and the 130kDa (gp130) subunit that by itself does not bind LIF, but is required for high affinity binding of LIF.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman



