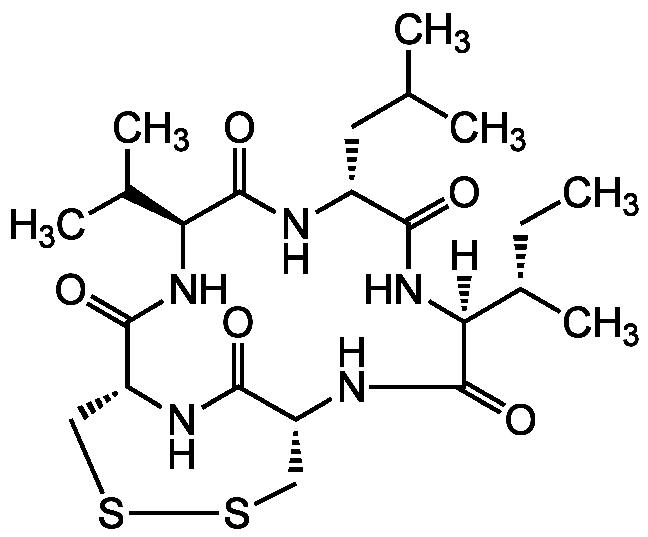
Chemical Structure
Malformin A1 [3022-92-2] [3022-92-2]
AG-CN2-0169
CAS Number3022-92-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight529.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameMalformin A1 [3022-92-2] [3022-92-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number3022-92-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC23H39N5O5S2
- Molecular Weight529.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 3022-92-2. Formula: C23H39N5O5S2. MW: 529.7. Synthetic. Originally isolated from Aspergillus niger. Peptide antibiotic. Antibcaterial. Plant growth stimulator. Induces root curvature and malformation in plants. Mycotoxin. Prevents interleukin-1 (IL-1) induced endothelial changes by inhibition of protein synthesis. Inhibitor of interleukin-1 beta (IL1 beta) binding to its receptor. Enhancer of cellular fibrinolytic activity. Disrupts the cell cycle at the G2 checkpoint of cancer cells, leading to sensitization of the cancer cells to anti-cancer reagents. Anticancer compound. Cytotoxic against several cancer cell lines. Antimalarial and antitrypanosomal. Inhibitor of BRAF-mutated melanoma cell lines. - Peptide antibiotic. Antibcaterial [1]. Plant growth stimulator [2]. Induces root curvature and malformation in plants [3]. Mycotoxin [4]. Prevents interleukin-1 (IL-1) induced endothelial changes by inhibition of protein synthesis [5]. Inhibitor of interleukin-1 beta (IL1 beta) binding to its receptor [6]. Enhancer of cellular fibrinolytic activity [7, 12]. Disrupts the cell cycle at the G2 checkpoint of cancer cells, leading to sensitization of the cancer cells to anti-cancer reagents [8]. Anticancer compound. Cytotoxic against several cancer cell lines [9]. Antimalarial and antitrypanosomal [10]. Inhibitor of BRAF-mutated melanoma cell lines [11].
- SMILES[H][C@]1(NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@H]2CSSC[C@@H](NC1=O)C(=O)N2)C(C)C)[C@@H](C)CC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Malformin A [3022-92-2] [3022-92-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/55/CgoaEGY7MB-EfuVZAAAAANj5lp8940.png)