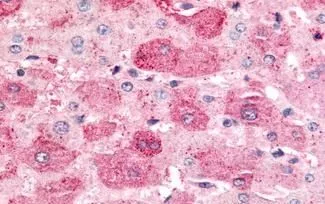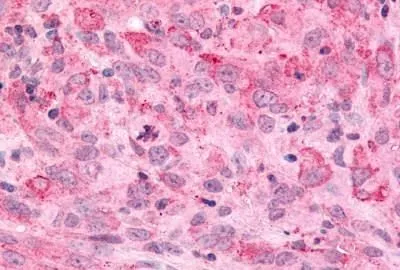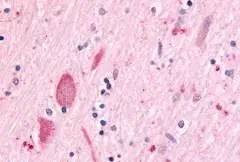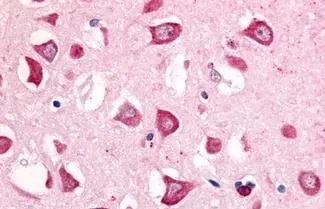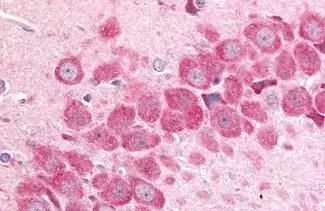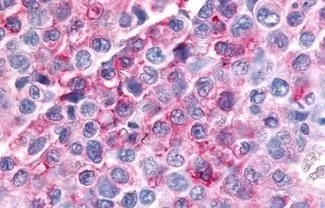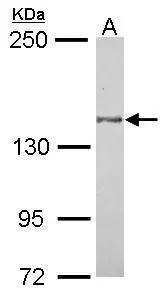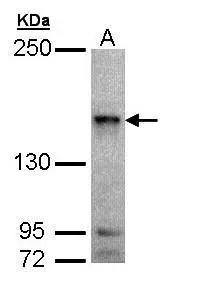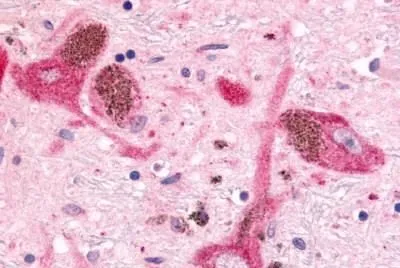
IHC-P analysis of brain, substantia nigra tissue using GTX70987 MAP4K6 antibody.
MAP4K6 antibody
GTX70987
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Equine, Human, Mammals, Monkey, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
TargetMINK1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMAP4K6 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 7 microg/ml. IHC-P: 7 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID50488
- Target nameMINK1
- Target descriptionmisshapen like kinase 1
- Target synonymsB55, MAP4K6, MEKKK 6, MINK, YSK2, ZC3, misshapen-like kinase 1, GCK family kinase MINK, MAPK/ERK kinase kinase kinase 6, MEK kinase kinase 6, misshapen/NIK-related kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 6
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8N4C8
- Protein NameMisshapen-like kinase 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the germinal center kinase (GCK) family. The protein is structurally similar to the kinases that are related to NIK and may belong to a distinct subfamily of NIK-related kinases within the GCK family. Studies of the mouse homolog indicate an up-regulation of expression in the course of postnatal mouse cerebral development and activation of the cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and the p38 pathways. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2016]
- ReactivityBovine, Equine, Human, Mammals, Monkey, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Hussain NK, Hsin H, Huganir RL, et al. MINK and TNIK differentially act on Rap2-mediated signal transduction to regulate neuronal structure and AMPA receptor function. J Neurosci. 2010,30(44):14786-94. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4124-10.2010Read this paper