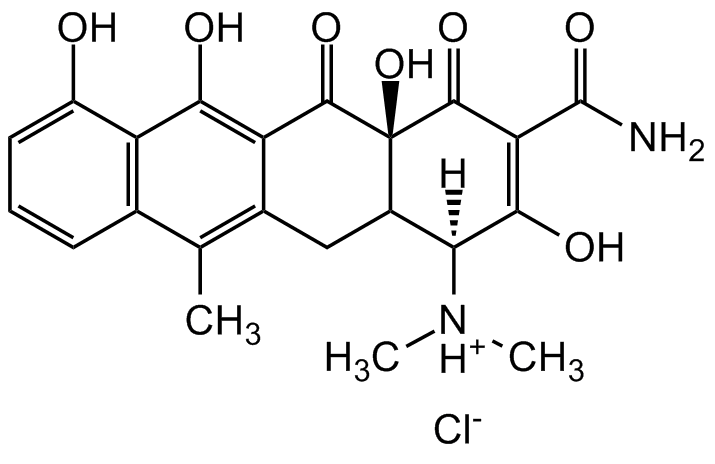
Minocycline hydrochloride [13614-98-7] [13614-98-7]
CDX-M0620
CAS Number13614-98-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight493.94
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameMinocycline hydrochloride [13614-98-7] [13614-98-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number13614-98-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC23H27N3O7 . HCl
- Molecular Weight493.94
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 13614-98-7. Formula: C23H27N3O7 . HCl. MW: 493.94. Minocycline, a semi-synthetic second-generation tetracycline, is a broad spectrum antibiotic with bacteriostatic function. Tetracyclines, including minocycline, function by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, thereby preventing charged tRNA from delivering amino acids to elongate the protein chain and form cellular protein. This disruption results in a bacteriostatic effect on the prokaryotic cell, leading to the loss of its ability to grow or replicate. Being lipid-soluble compounds, tetracyclines can traverse hydrophobic barriers such as biological membranes. It is orally active and brain penetrant. Apart from its efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, minocycline also exhibits antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties. Minocycline has anti-inflammatory properties and inhibits neuroinflammation in pre-plaque of Alzheimers disease-like amyloid pathology through inhibition of key inflammatory enzymes like inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and 5-lipoxygenase. Minocycline inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis, and inhibit the enzymatic activity of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Minocycline exhibits anti-tumor activity in glioma by inhibiting membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). Minocycline increases cognition and neuronal differentiation. - Minocycline, a semi-synthetic second-generation tetracycline, is a broad spectrum antibiotic with bacteriostatic function. Tetracyclines, including minocycline, function by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, thereby preventing charged tRNA from delivering amino acids to elongate the protein chain and form cellular protein. This disruption results in a bacteriostatic effect on the prokaryotic cell, leading to the loss of its ability to grow or replicate. Being lipid-soluble compounds, tetracyclines can traverse hydrophobic barriers such as biological membranes. It is orally active and brain penetrant. Apart from its efficacy against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, minocycline also exhibits antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective properties. Minocycline has anti-inflammatory properties and inhibits neuroinflammation in pre-plaque of Alzheimers disease-like amyloid pathology through inhibition of key inflammatory enzymes like inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and 5-lipoxygenase. Minocycline inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis, and inhibit the enzymatic activity of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1). Minocycline exhibits anti-tumor activity in glioma by inhibiting membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). Minocycline increases cognition and neuronal differentiation.
- SMILESCN(C)[C@H](C(O)=C1C(N)=O)[C@@]2([H])[C@@](C(O)=C(C(C3=C(O)C=CC(N(C)C)=C3C4)=O)[C@]4([H])C2)(O)C1=O.Cl
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200