Chemical Structure
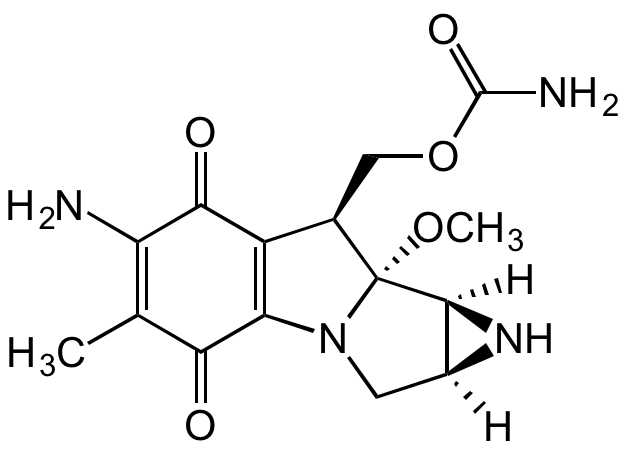
Mitomycin C [50-07-7] [50-07-7]
CDX-M0161
CAS Number50-07-7
Product group Chemicals
Molecular Weight334.33
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameMitomycin C [50-07-7] [50-07-7]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number50-07-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC15H18N4O5
- Molecular Weight334.33
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 50-07-7. Formula: C15H18N4O5. MW: 334.33. Mitomycin C (MMC) is an antitumor antibiotic. This product is an alkylating agent that specifically targets the guanine nucleoside sequence 5-CpG-3. It inhibits DNA synthesis by covalently reacting with DNA, forming crosslinks between complementary strands of DNA. This interaction prevents separation of complementary DNA strands, inhibiting DNA replication. Mitomycin C causes the cross-linking of double-stranded DNA, which results in mutagenesis, inhibition of DNA synthesis, initiation of DNA repair events, and activation of apoptosis. In tissue culture, this compound decreases cell viability and suppresses mitosis, and causes disorganization of nucleus and the production of giant cells. Mitomycin C has strong antitumor activity, especially against Ehrlich ascites tumor cells, and strong bactericidal action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Mitomycin C from Streptomyces caespitosus has been used for the treatment of feeder layers such as, PMEF (primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts) and CD1 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) for the culture of hESCs (human embryonic stem cells). It has also been used for the treatment of BLC (basal-like cancer) cell line. - Mitomycin C (MMC) is an antitumor antibiotic. This product is an alkylating agent that specifically targets the guanine nucleoside sequence 5-CpG-3. It inhibits DNA synthesis by covalently reacting with DNA, forming crosslinks between complementary strands of DNA. This interaction prevents separation of complementary DNA strands, inhibiting DNA replication. Mitomycin C causes the cross-linking of double-stranded DNA, which results in mutagenesis, inhibition of DNA synthesis, initiation of DNA repair events, and activation of apoptosis. In tissue culture, this compound decreases cell viability and suppresses mitosis, and causes disorganization of nucleus and the production of giant cells. Mitomycin C has strong antitumor activity, especially against Ehrlich ascites tumor cells, and strong bactericidal action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Mitomycin C from Streptomyces caespitosus has been used for the treatment of feeder layers such as, PMEF (primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts) and CD1 mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) for the culture of hESCs (human embryonic stem cells). It has also been used for the treatment of BLC (basal-like cancer) cell line.
- SMILESNC1=C(C)C(C(N(C[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])N2)[C@@]3(OC)[C@@H]4COC(N)=O)=C4C1=O)=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Mitomycin C [50-07-7]](https://bpsbioscience.com/media/catalog/product/m/i/mitomycin_c.png)

