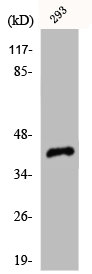
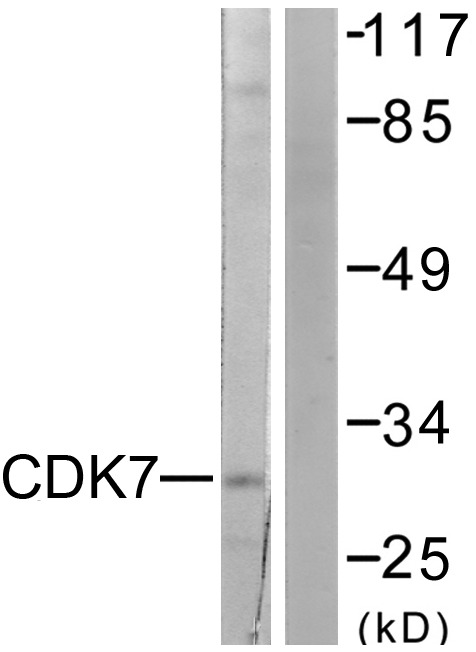
Mouse anti Human Cyclin Dependant Kinase 7
C145M
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCDK7
Product C145M is not available
Product not available
There may be an alternative product available, please contact our technical support team.
Overview
- SupplierNordic-MUbio
- Product NameMouse anti Human Cyclin Dependant Kinase 7
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteApplications: 1-10 ug/ml for Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- Applications SupplierWestern Blotting;Immunoprecipitation;Immunohistochemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDMO-1
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1022
- Target nameCDK7
- Target descriptioncyclin dependent kinase 7
- Target synonymsCAK, CAK1, CDKN7, HCAK, MO15, STK1, p39MO15, cyclin-dependent kinase 7, 39 KDa protein kinase, CDK-activating kinase 1, TFIIH basal transcription factor complex kinase subunit, cell division protein kinase 7, cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (MO15 homolog, Xenopus laevis, cdk-activating kinase), homolog of Xenopus MO15 Cdk-activating kinase, kinase subunit of CAK, serine/threonine kinase stk1, serine/threonine protein kinase 1, serine/threonine protein kinase MO15
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP50613
- Protein NameCyclin-dependent kinase 7
- Scientific DescriptionCyclin dependant kinase 7; cdk7; CDK-activating kinase; CAK; TFIIH basal transcription factor complex kinase subunit
- Shelf life instructionSee expiration date on vial
- SourceRabbits were immunized with a recombinant 221 amino acid fragment of the C terminus of p40mo15 recognizing a 40kD protein
- ReactivityHuman
- Reactivity SupplierHuman
- UNSPSC12352203