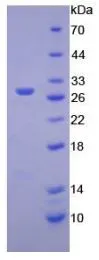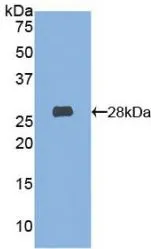
WB analysis of GTX00306-pro Mouse HEXA protein.
Mouse HEXA protein, His tag
GTX00306-PRO
Product group Molecular Biology
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMouse HEXA protein (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
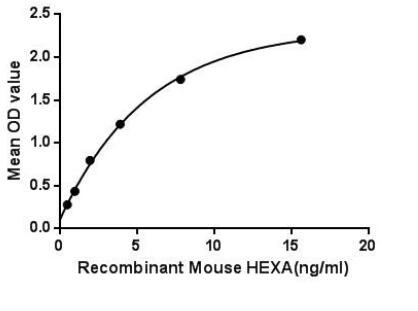
- Application Supplier NoteHexosaminidase A Alpha (HEXa) is a lysosomal enzyme. There are three predominant isoenzymes: hexosaminidase A, B and S. Hexosaminidase A and the cofactor GM2 activator protein catalyze the degradation of the GM2 gangliosides and other molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines. The enzymes are composed of two alpha and/or beta subunits, which are coded by HEXA and HEXB genes, respectively. Even though the alpha and beta subunits of hexosaminidase A can both cleave GalNAc residues, only the alpha subunit which contains a key residue, Arg-424 is able to hydrolyze GM2 gangliosides. Hexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide) plays a critical role in the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system). Besides, Hexosaminidase B Beta (HEXB) has been identified as an interactor of HEXA, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant mouse HEXA and recombinant mouse HEXB. Briefly, HEXA were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to HEXB-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-HEXA pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of of HEXA and HEXB was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the glycosyl hydrolase 20 family of proteins. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the alpha subunit of the lysosomal enzyme beta-hexosaminidase. This enzyme, together with the cofactor GM2 activator protein, catalyzes the degradation of the ganglioside GM2, and other molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines. Mice lacking the encoded protein exhibit accumulation of gangliosides in the brain and membranous cytoplasmic bodies in neurons. Certain mutations in the human ortholog of this gene cause Tay-Sachs disease. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2016]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352204