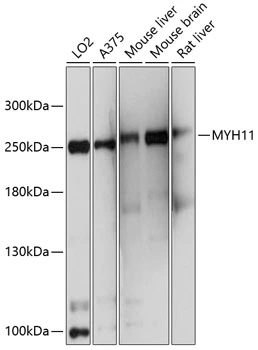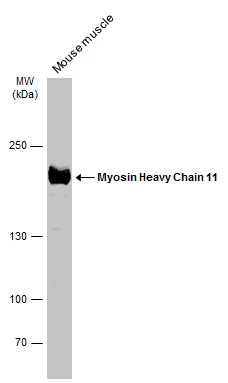
Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Myosin Heavy Chain 11 antibody (GTX131414) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
Myosin Heavy Chain 11 antibody
GTX131414
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetMYH11
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMyosin Heavy Chain 11 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.85 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4629
- Target nameMYH11
- Target descriptionmyosin heavy chain 11
- Target synonymsAAT4, FAA4, SMHC, SMMHC, SMMS-1, VSCM2, myosin-11, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, myosin, heavy chain 11, smooth muscle, myosin, heavy polypeptide 11, smooth muscle
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP35749
- Protein NameMyosin-11
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a smooth muscle myosin belonging to the myosin heavy chain family. The gene product is a subunit of a hexameric protein that consists of two heavy chain subunits and two pairs of non-identical light chain subunits. It functions as a major contractile protein, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy through the hydrolysis of ATP. The gene encoding a human ortholog of rat NUDE1 is transcribed from the reverse strand of this gene, and its 3 end overlaps with that of the latter. The pericentric inversion of chromosome 16 [inv(16)(p13q22)] produces a chimeric transcript that encodes a protein consisting of the first 165 residues from the N terminus of core-binding factor beta in a fusion with the C-terminal portion of the smooth muscle myosin heavy chain. This chromosomal rearrangement is associated with acute myeloid leukemia of the M4Eo subtype. Alternative splicing generates isoforms that are differentially expressed, with ratios changing during muscle cell maturation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161