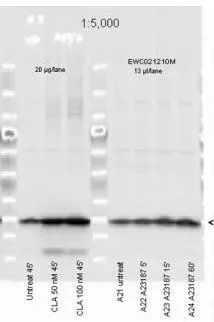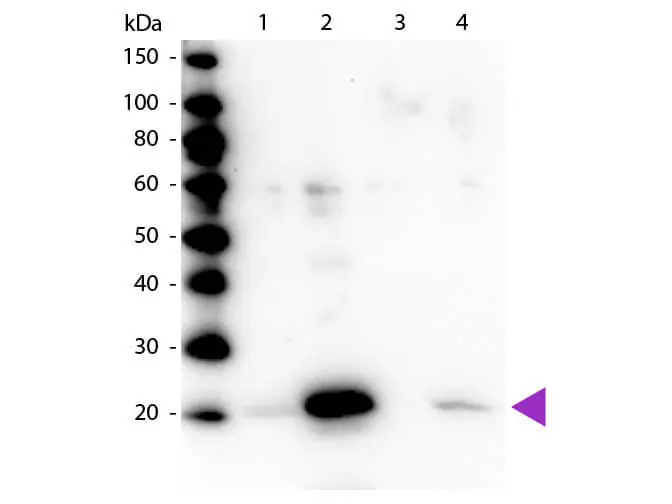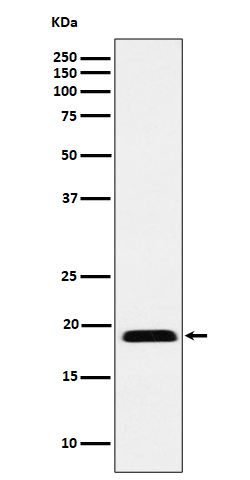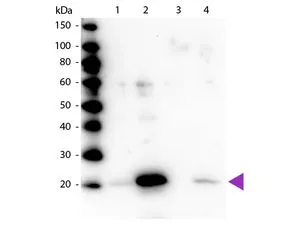
Western blot of Myosin Light chain (phospho Ser20) antibody (GTX22480). Lane 1: Regulatory Light Chain Non-Phospho recombinant protein. Lane 2: Regulatory Light Chain Phospho recombinant protein. Lane 3: Smooth Muscle Non-Phospho recombinant protein. Lane 4: Smooth Muscle Phospho recombinant protein. Load: 50 ng per lane. Primary antibody at 1:1,000 overnight at 4oC. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase rabbit secondary antibody at 1:40,000 for 60 min at RT. Blocking for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 20 kDa.
Myosin Light Chain 2 (phospho Ser19) antibody
GTX22480
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetMYL12A
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMyosin Light Chain 2 (phospho Ser19) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:2000. IHC-P: 2-5 microg/mL. IP: 1:100. ELISA: 1:10000-1:30000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.19 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10627
- Target nameMYL12A
- Target descriptionmyosin light chain 12A
- Target synonymsHEL-S-24, MLC-2B, MLCB, MRCL3, MRLC3, MYL2B, myosin regulatory light chain 12A, epididymis secretory protein Li 24, myosin RLC, myosin regulatory light chain 2, nonsarcomeric, myosin regulatory light chain 3, myosin regulatory light chain MRLC3, myosin, light chain 12A, regulatory, non-sarcomeric, myosin, light polypeptide, regulatory, non-sarcomeric (20kD)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO14950
- Protein NameMyosin regulatory light chain 12B
- Scientific DescriptionMyosin is the major component of thick muscle filaments, and is a long asymmetric molecule containing a globular head and a long tail. The molecule consists of two heavy chains each ~200,000 daltons, and four light chains each ~16,000 - 21,000 daltons. Activation of smooth and cardiac muscle primarily involves pathways that increase calcium levels and myosin phosphorylation, resulting in contraction. Myosin light chain phosphatase acts to regulate muscle contraction by dephosphorylating activated myosin light chain. This antibody is specific for the phosphorylated form of myosin light chain. The selected peptide sequence used to generate the polyclonal antibody is located near the amino terminal end of the polypeptide corresponding to the smooth/non-muscle form of myosin regulatory light chain found in cardiac myocytes in addition to smooth and non-muscle cells. This sequence differs from that of the sarcomeric/cardiac form of myosin regulatory light chain that has a different sequence around the phosphorylation site. Human and mouse have almost identical sequences. In human the phosphorylation site is pS19, while in mouse the site maps to pS20.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
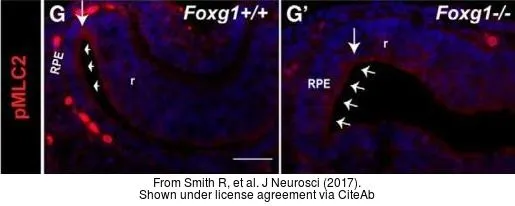
- The Transcription Factor Foxg1 Promotes Optic Fissure Closure in the Mouse by Suppressing Wnt8b in the Nasal Optic Stalk. Smith R et al., 2017 Aug 16, J NeurosciRead this paper
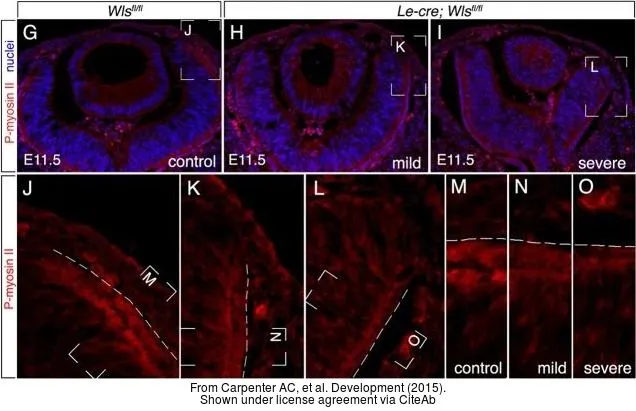
- Wnt ligands from the embryonic surface ectoderm regulate bimetallic strip optic cup morphogenesis in mouse. Carpenter AC et al., 2015 Mar 1, DevelopmentRead this paper
- A Trio-RhoA-Shroom3 pathway is required for apical constriction and epithelial invagination. Plageman TF Jr et al., 2011 Dec, DevelopmentRead this paper
- Balanced Rac1 and RhoA activities regulate cell shape and drive invagination morphogenesis in epithelia. Chauhan BK et al., 2011 Nov 8, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S ARead this paper
- Cdc42- and IRSp53-dependent contractile filopodia tether presumptive lens and retina to coordinate epithelial invagination. Chauhan BK et al., 2009 Nov, DevelopmentRead this paper