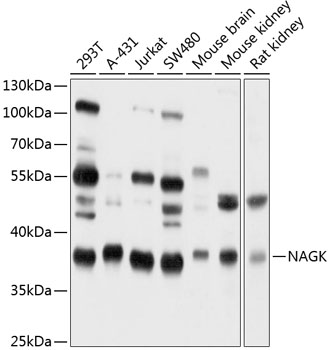
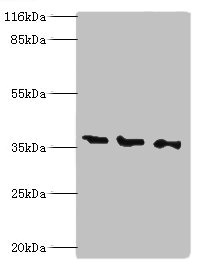
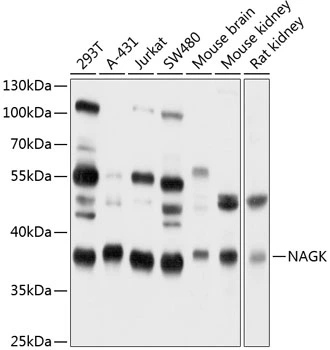
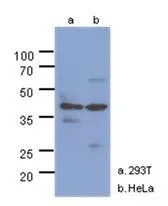
NAGK antibody
GTX116238
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Rat
TargetNAGK
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNAGK antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID55577
- Target nameNAGK
- Target descriptionN-acetylglucosamine kinase
- Target synonymsGNK, HSA242910, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine kinase, N-acetyl-D-mannosamine kinase, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, glcNAc kinase, muramyl dipeptide kinase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UJ70
- Protein NameN-acetyl-D-glucosamine kinase
- Scientific DescriptionN-acetylglucosamine kinase (NAGK; EC 2.7.1.59) converts endogenous N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), a major component of complex carbohydrates, from lysosomal degradation or nutritional sources into GlcNAc 6-phosphate. NAGK belongs to the group of N-acetylhexosamine kinases and is a prominent salvage enzyme of amino sugar metabolism in mammals.[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161